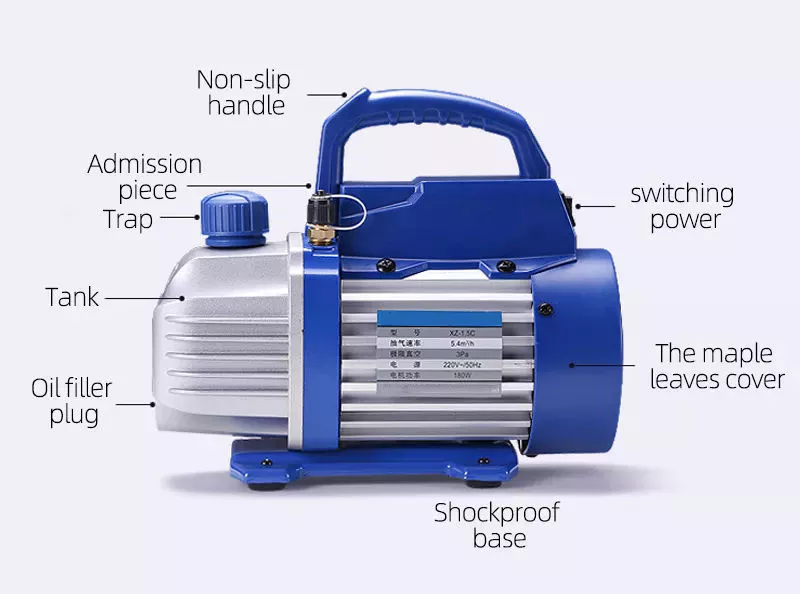
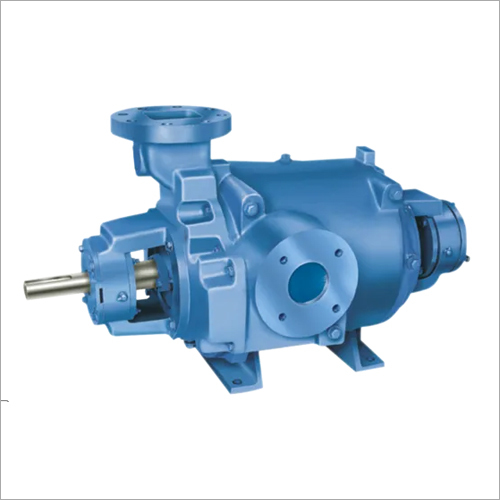
Product Description
2XZ-2
Physical Property
| Voltage | 220V/50HZ | Displacement | 4CFM |
| Voltage | 110V/60HZ | Displacement | 6CFM |
| Ultimate Vacuum | 6X10-2PA | Motor Power | 1/2HP |
| Fuel | Electric | Oil Capacity | 1000ML |
| Dimension | 514X168X282mm | Usage | Air Pump |
| Structure | Double-stage Vacuum Pump | Color | Black |
| N.W.(1 Set) | 22Kg | Package Size | 60X21X32cm |
Application
The application is wide, such as vacuum refrigeration, refrigerant recovery device, tea packaging, air conditioner, automobile reparation, medical research equipment, packaging and printing equipment, scientific research, semi-conductor and etc.
Main Features
1) It can work in low temperature environment,even in cold winter.
2) Unlike the traditional ones ,RS series are much lighter,which is easy to carry.
3) RS series are attractive design in its outlook,looks more fashionable.
HangZhou CZPT Refrigeration Technology Co., Ltd. is a large modern chemical enterprise specializing in manufacturing, researching and exporting high purity fluoro-chemicals, fine chemicals, hydrocarbon chemicals, etc. Its headquarter locates in ZheJiang capital HangZhou city, and has 2 profound manufacturing bases, separately in HangZhou City of ZheJiang Province and HangZhou city of ZHangZhoug Province. Our company takes “Science and Technology, Environmental Protection, Internationalization” as development direction and “First-class Technology, First-class Quality, First-class Service, First-class Efficiency” as service tenet.
Main Products:
R22 , R134A , R410A , R407c , R507 , R404A , R600 Refrigerant Gas, Manifold Gauge ,vacuum pump, compressor, etc.
Customer’s satisfactory is our forever pursue
FAQ
Q: If there’s space for you to lower the price?
A: The price in that field is changeable, so, fell free to ask for latest price and I’ll provide you the lowest.
Q: Could I use my own LOGO or design on the goods?
A: Of course, Customized logo and design on mass production are available.
Q: Can I visit your factory?
A: Sure, you can come at any time. We can also pick you up at airport or at the station.
Q: What is the delivery time?
A: One week for sample, 15 to 20 days for mass production.
Q: How about the payment term?
A: TT, L/C at sight, Paypal, Western Union, etc. Normally 30% T/T in advance, 30% TT before shipment, the balance against the copy of B/L in 7 days.
Q: How much discount can you offer?
A: We will do our best to offer the competitive price, the discount usually depends on the quantity.
Q: The shipping fare costs too much ,can you make it cheaper for us?
A: We will try our best to negotiate with shipping company,we save every penny for our customers,if it is possible ,you can designate your own shipping agency.
Q: Can I trust you?
A: Absolutely YES. We are “made in china” verified supplier.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Oil or Not: | Oil Free |
|---|---|
| Structure: | Rotary Vacuum Pump |
| Working Conditions: | Dry |
| Ultimate Vacuum: | 6X10-2PA |
| Power: | 1/2HP |
| Fuel: | Electric |
| Samples: |
US$ 180/Set
1 Set(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
Basic knowledge of vacuum pump
A vacuum pump is a device that draws gas molecules from a sealed volume and maintains a partial vacuum. Its main job is to create a relative vacuum within a given volume or volumes. There are many types of vacuum pumps. This article will describe how they work, their types, and their applications.
How it works
A vacuum pump is a mechanical device that removes gas from a system by applying it to a higher pressure than the surrounding atmosphere. The working principle of the vacuum pump is based on the principle of gas transfer and entrapment. Vacuum pumps can be classified according to their vacuum level and the number of molecules that can be removed per cubic centimeter of space. In medium to high vacuum, viscous flow occurs when gas molecules collide with each other. Increasing the vacuum causes molecular or transitional flow.
A vacuum pump has several components that make it a versatile tool. One of the main components is the motor, which consists of a rotor and a stator. The rotor and stator contain coils that generate a magnetic field when excited. Both parts must be mounted on a base that supports the weight of the pump. There is also an oil drain that circulates oil throughout the system for lubrication and cooling purposes.
Another type of vacuum pump is the liquid ring vacuum pump. It works by positioning the impeller above or below the blades. Liquid ring pumps can also adjust the speed of the impeller. However, if you plan to use this type of pump, it is advisable to consult a specialist.
Vacuum pumps work by moving gas molecules to areas of higher or lower pressure. As the pressure decreases, the removal of the molecules becomes more difficult. Industrial vacuum systems require pumps capable of operating in the 1 to 10-6 Torr range.
Type
There are different types of vacuum pumps. They are used in many different applications, such as laboratories. The main purpose of these pumps is to remove air or gas molecules from the vacuum chamber. Different types of pumps use different techniques to achieve this. Some types of pumps use positive displacement, while others use liquid ring, molecular transfer, and entrapment techniques.
Some of these pumps are used in industrial processes, including making vacuum tubes, CRTs, electric lights, and semiconductor processing. They are also used in motor vehicles to power hydraulic components and aircraft. The gyroscope is usually controlled by these pumps. In some cases, they are also used in medical settings.
How a vacuum pump works depends on the type of gas being pumped. There are three main types: positive displacement, negative displacement, and momentum transfer. Depending on the type of lubrication, these principles can be further divided into different types of pumps. For example, dry vacuum pumps are less sensitive to gases and vapors.
Another type of vacuum pump is called a rotary vane pump. This type of pump has two main components, the rotor and the vacuum chamber. These pumps work by rotating moving parts against the pump casing. The mating surfaces of rotary pumps are designed with very small clearances to prevent fluid leakage to the low pressure side. They are suitable for vacuum applications requiring low pulsation and high continuous flow. However, they are not suitable for use with grinding media.
There are many types of vacuum pumps and it is important to choose the right one for your application. The type of pump depends on the needs and purpose of the system. The larger ones can work continuously, and the smaller ones are more suitable for intermittent use. 
Apply
Vacuum pumps are used in a variety of industrial and scientific processes. For example, they are used in the production of vacuum tubes, CRTs, and electric lamps. They are also used in semiconductor processing. Vacuum pumps are also used as mechanical supports for other equipment. For example, there may be multiple vacuum pumps on the engine of a motor vehicle that powers the hydraulic components of an aircraft. In addition, they are often used in fusion research.
The most common type of vacuum pump used in the laboratory is the rotary vane pump. It works by directing airflow through a series of rotating blades in a circular housing. As the blades pass through the casing, they remove gas from the cavity and create a vacuum. Rotary pumps are usually single or double-stage and can handle pressures between 10 and 6 bar. It also has a high pumping speed.
Vacuum pumps are also used to fabricate solar cells on wafers. This involves a range of processes including doping, diffusion, dry etching, plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition, and bulk powder generation. These applications depend on the type of vacuum pump used in the process, and the vacuum pump chosen should be designed for the environment.
While there are several types of vacuum pumps available, their basic working principles remain the same. Each has different functions and capacities, depending on the type of vacuum. Generally divided into positive displacement pump, rotary vane pump, liquid ring pump, and molecular delivery pump.
Maintenance
The party responsible for general maintenance and repairs is the Principal Investigator (PI). Agknxs must be followed and approved by the PI and other relevant laboratory personnel. The Agknx provides guidelines for routine maintenance of vacuum pump equipment. Agknxs are not intended to replace detailed routine inspections of vacuum pump equipment, which should be performed by certified/qualified service personnel. If the device fails, the user should contact PI or RP for assistance.
First, check the vacuum pump for any loose parts. Make sure the inlet and outlet pressure gauges are open. When the proper pressure is shown, open the gate valve. Also, check the vacuum pump head and flow. Flow and head should be within the range indicated on the label. Bearing temperature should be within 35°F and maximum temperature should not exceed 80°F. The vacuum pump bushing should be replaced when it is severely worn.
If the vacuum pump has experienced several abnormal operating conditions, a performance test should be performed. Results should be compared to reference values to identify abnormalities. To avoid premature pump failure, a systematic approach to predictive maintenance is essential. This is a relatively new area in the semiconductor industry, but leading semiconductor companies and major vacuum pump suppliers have yet to develop a consistent approach.
A simplified pump-down test method is proposed to evaluate the performance of vacuum pumps. The method includes simulated aeration field tests and four pump performance indicators. Performance metrics are evaluated under gas-loaded, idle, and gas-load-dependent test conditions. 
Cost
The total cost of a vacuum pump consists of two main components: the initial investment and ongoing maintenance costs. The latter is the most expensive component, as it consumes about four to five times the initial investment. Therefore, choosing a more energy-efficient model is a good way to reduce the total system cost and payback period.
The initial cost of a vacuum pump is about $786. Oil-lubricated rotary vane pumps are the cheapest, while oil-free rotary vane pumps are slightly more expensive. Non-contact pumps also cost slightly more. The cost of a vacuum pump is not high, but it is a factor that needs careful consideration.
When choosing a vacuum pump, it is important to consider the type of gas being pumped. Some pumps are only suitable for pumping air, while others are designed to pump helium. Oil-free air has a different pumping rate profile than air. Therefore, you need to consider the characteristics of the medium to ensure that the pump meets your requirements. The cost of a vacuum pump can be much higher than the purchase price, as the daily running and maintenance costs can be much higher.
Lubricated vacuum pumps tend to be more durable and less expensive, but they may require more maintenance. Maintenance costs will depend on the type of gas that needs to be pumped. Lighter gases need to be pumped slowly, while heavier gases need to be pumped faster. The maintenance level of a vacuum pump also depends on how often it needs to be lubricated.
Diaphragm vacuum pumps require regular maintenance and oil changes. The oil in the diaphragm pump should be changed every 3000 hours of use. The pump is also resistant to chemicals and corrosion. Therefore, it can be used in acidic and viscous products.


editor by Dream 2024-05-16
China manufacturer China Foundry Wholesale High Quality Customize Service Slurry Pump, Vacuum Pump, Submersible Pump, Pump Spare Parts vacuum pump adapter
Product Description
OEM Pump Support Housing, Pump Motor Body, Cast Iron Casting, Quality Casting Manufacturer
With our automatic sand molding line, it great improve the iron casting quality ,save the manufacturing cost, and help the lead time.
We can supply very competitive price with good quality, fast lead time, efficient quotation, feel free to email us the RFQ for CHINAMFG parts.
We have 2 factory shops for sand casting products,cast from the material of cast iron, ductile iron casting, aluminum, brass. We have both towering CHINAMFG for big melting volume and intermediate frequency furnaces for less melting volume. The annual output capability is more than 1000 tons. Our mainly sand casting parts is: for the diesel oil vehicles of engine body and impeller, various water pump body and housing, for the food industry machine, such as tomato mill machine parts of body and Spiral, meat mincer machine parts of body,Spiral and ring. We also can cast the big body for grinding or lathe machine.
We can supply official Material Chemical report, Tenstile testing report.
FAQ
1.What do you need to provide a quote?
Please kindly send us the drawing of your product. Details below should be included,
A.Materials B. Surface Finish C. Tolerance D. Quantity
(Please be noted that these are essential for our quoting. We couldn’t quote the specific
price without any of them.).
2.When can I get the price?
Our professional sales team will feedback your RFQ within 12hours, and give you the Quotation within 48hours max. if the drawing and specification is all in details.
3.How can I get the sample to check your quality?
After price confirmation, you can require for samples to check our product’s quality. If you just need a blank sample to check the manufacturing quality, we will provide you sample after the sample order confirmed.
4.What’s the lead time for Mould and samples ?
For normal project, we can complete Mould and supply the 1st article sample within 30 to 40days.
For urgently project, we can complete the Mould and Sample within 20days max.
5.What’s the payment terms for Order ?
For Mould/tooling and sample : 50% deposit pay by Order, rest 50% pay after sample approval.
For production Order for new Customers : we request 30% down payment, rest 70% pay by copy of Original B/L copy. For long lasting regular customer, we can give better payment terms, such as 100% pay after delivery or by B/L copy.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Type: | Clay Dry Sand |
|---|---|
| Casting Method: | Aluminum Sand Casting |
| Sand Core Type: | Resin Sand Core |
| Application: | Machinery Parts |
| Machining: | CNC Machining |
| Material: | Aluminum A356 |
| Samples: |
US$ 30/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

Can Vacuum Pumps Be Used in the Automotive Industry?
Yes, vacuum pumps are widely used in the automotive industry for various applications. Here’s a detailed explanation:
The automotive industry relies on vacuum pumps for several critical functions and systems within vehicles. Vacuum pumps play a crucial role in enhancing performance, improving fuel efficiency, and enabling the operation of various automotive systems. Here are some key applications of vacuum pumps in the automotive industry:
1. Brake Systems: Vacuum pumps are commonly used in vacuum-assisted brake systems, also known as power brakes. These systems utilize vacuum pressure to amplify the force applied by the driver to the brake pedal, making braking more efficient and responsive. Vacuum pumps help generate the required vacuum for power brake assistance, ensuring reliable and consistent braking performance.
2. Emission Control Systems: Vacuum pumps are integral components of emission control systems in vehicles. They assist in operating components such as the Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) valve and the Evaporative Emission Control (EVAP) system. Vacuum pumps help create the necessary vacuum conditions for proper functioning of these systems, reducing harmful emissions and improving overall environmental performance.
3. HVAC Systems: Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) systems in vehicles often utilize vacuum pumps for various functions. Vacuum pumps help control the vacuum-operated actuators that regulate the direction, temperature, and airflow of the HVAC system. They ensure efficient operation and precise control of the vehicle’s interior climate control system.
4. Turbocharger and Supercharger Systems: In performance-oriented vehicles, turbocharger and supercharger systems are used to increase engine power and efficiency. Vacuum pumps play a role in these systems by providing vacuum pressure for actuating wastegates, blow-off valves, and other control mechanisms. These components help regulate the boost pressure and ensure optimal performance of the forced induction system.
5. Fuel Delivery Systems: Vacuum pumps are employed in certain types of fuel delivery systems, such as mechanical fuel pumps. These pumps utilize vacuum pressure to draw fuel from the fuel tank and deliver it to the engine. While mechanical fuel pumps are less commonly used in modern vehicles, vacuum pumps are still found in some specialized applications.
6. Engine Management Systems: Vacuum pumps are utilized in engine management systems for various functions. They assist in operating components such as vacuum-operated actuators, vacuum reservoirs, and vacuum sensors. These components play a role in engine performance, emissions control, and overall system functionality.
7. Fluid Control Systems: Vacuum pumps are used in fluid control systems within vehicles, such as power steering systems. Vacuum-assisted power steering systems utilize vacuum pressure to assist the driver in steering, reducing the effort required. Vacuum pumps provide the necessary vacuum for power steering assistance, enhancing maneuverability and driver comfort.
8. Diagnostic and Testing Equipment: Vacuum pumps are also utilized in automotive diagnostic and testing equipment. These pumps create vacuum conditions necessary for testing and diagnosing various vehicle systems, such as intake manifold leaks, brake system integrity, and vacuum-operated components.
It’s important to note that different types of vacuum pumps may be used depending on the specific automotive application. Common vacuum pump technologies in the automotive industry include diaphragm pumps, rotary vane pumps, and electric vacuum pumps.
In summary, vacuum pumps have numerous applications in the automotive industry, ranging from brake systems and emission control to HVAC systems and engine management. They contribute to improved safety, fuel efficiency, environmental performance, and overall vehicle functionality.

How Do Vacuum Pumps Contribute to Energy Savings?
Vacuum pumps play a significant role in energy savings in various industries and applications. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Vacuum pumps contribute to energy savings through several mechanisms and efficiencies. Some of the key ways in which vacuum pumps help conserve energy are:
1. Improved Process Efficiency: Vacuum pumps are often used to remove gases and create low-pressure or vacuum conditions in industrial processes. By reducing the pressure, vacuum pumps enable the removal of unwanted gases or vapors, improving the efficiency of the process. For example, in distillation or evaporation processes, vacuum pumps help lower the boiling points of liquids, allowing them to evaporate or distill at lower temperatures. This results in energy savings as less heat is required to achieve the desired separation or concentration.
2. Reduced Energy Consumption: Vacuum pumps are designed to operate efficiently and consume less energy compared to other types of equipment that perform similar functions. Modern vacuum pump designs incorporate advanced technologies, such as variable speed drives, energy-efficient motors, and optimized control systems. These features allow vacuum pumps to adjust their operation based on demand, reducing energy consumption during periods of lower process requirements. By consuming less energy, vacuum pumps contribute to overall energy savings in industrial operations.
3. Leak Detection and Reduction: Vacuum pumps are often used in leak detection processes to identify and locate leaks in systems or equipment. By creating a vacuum or low-pressure environment, vacuum pumps can assess the integrity of a system and identify any sources of leakage. Detecting and repairing leaks promptly helps prevent energy wastage associated with the loss of pressurized fluids or gases. By addressing leaks, vacuum pumps assist in reducing energy losses and improving the overall energy efficiency of the system.
4. Energy Recovery Systems: In some applications, vacuum pumps can be integrated into energy recovery systems. For instance, in certain manufacturing processes, the exhaust gases from vacuum pumps may contain heat or have the potential for energy recovery. By utilizing heat exchangers or other heat recovery systems, the thermal energy from the exhaust gases can be captured and reused to preheat incoming fluids or provide heat to other parts of the process. This energy recovery approach further enhances the overall energy efficiency by utilizing waste heat that would otherwise be lost.
5. System Optimization and Control: Vacuum pumps are often integrated into centralized vacuum systems that serve multiple processes or equipment. These systems allow for better control, monitoring, and optimization of the vacuum generation and distribution. By centralizing the vacuum production and employing intelligent control strategies, energy consumption can be optimized based on the specific process requirements. This ensures that vacuum pumps operate at the most efficient levels, resulting in energy savings.
6. Maintenance and Service: Proper maintenance and regular servicing of vacuum pumps are essential for their optimal performance and energy efficiency. Routine maintenance includes tasks such as cleaning, lubrication, and inspection of pump components. Well-maintained pumps operate more efficiently, reducing energy consumption. Additionally, prompt repair of any faulty parts or addressing performance issues helps maintain the pump’s efficiency and prevents energy waste.
In summary, vacuum pumps contribute to energy savings through improved process efficiency, reduced energy consumption, leak detection and reduction, integration with energy recovery systems, system optimization and control, as well as proper maintenance and service. By utilizing vacuum pumps efficiently and effectively, industries can minimize energy waste, optimize energy usage, and achieve significant energy savings in various applications and processes.

What Are the Primary Applications of Vacuum Pumps?
Vacuum pumps have a wide range of applications across various industries. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Industrial Processes:
Vacuum pumps play a vital role in numerous industrial processes, including:
– Vacuum Distillation: Vacuum pumps are used in distillation processes to lower the boiling points of substances, enabling separation and purification of various chemicals and compounds.
– Vacuum Drying: Vacuum pumps aid in drying processes by creating a low-pressure environment, which accelerates moisture removal from materials without excessive heat.
– Vacuum Packaging: Vacuum pumps are used in the food industry to remove air from packaging containers, prolonging the shelf life of perishable goods by reducing oxygen exposure.
– Vacuum Filtration: Filtration processes can benefit from vacuum pumps to enhance filtration rates by applying suction, facilitating faster separation of solids and liquids.
2. Laboratory and Research:
Vacuum pumps are extensively used in laboratories and research facilities for various applications:
– Vacuum Chambers: Vacuum pumps create controlled low-pressure environments within chambers for conducting experiments, testing materials, or simulating specific conditions.
– Mass Spectrometry: Mass spectrometers often utilize vacuum pumps to create the necessary vacuum conditions for ionization and analysis of samples.
– Freeze Drying: Vacuum pumps enable freeze-drying processes, where samples are frozen and then subjected to a vacuum, allowing the frozen water to sublimate directly from solid to vapor state.
– Electron Microscopy: Vacuum pumps are essential for electron microscopy techniques, providing the necessary vacuum environment for high-resolution imaging of samples.
3. Semiconductor and Electronics Industries:
High vacuum pumps are critical in the semiconductor and electronics industries for manufacturing and testing processes:
– Semiconductor Fabrication: Vacuum pumps are used in various stages of chip manufacturing, including deposition, etching, and ion implantation processes.
– Thin Film Deposition: Vacuum pumps create the required vacuum conditions for depositing thin films of materials onto substrates, as done in the production of solar panels, optical coatings, and electronic components.
– Leak Detection: Vacuum pumps are utilized in leak testing applications to detect and locate leaks in electronic components, systems, or pipelines.
4. Medical and Healthcare:
Vacuum pumps have several applications in the medical and healthcare sectors:
– Vacuum Assisted Wound Closure: Vacuum pumps are used in negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT), where they create a controlled vacuum environment to promote wound healing and removal of excess fluids.
– Laboratory Equipment: Vacuum pumps are essential in medical and scientific equipment such as vacuum ovens, freeze dryers, and centrifugal concentrators.
– Anesthesia and Medical Suction: Vacuum pumps are utilized in anesthesia machines and medical suction devices to create suction and remove fluids or gases from the patient’s body.
5. HVAC and Refrigeration:
Vacuum pumps are employed in the HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) and refrigeration industries:
– Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Systems: Vacuum pumps are used during system installation, maintenance, and repair to evacuate moisture and air from refrigeration and air conditioning systems, ensuring efficient operation.
– Vacuum Insulation Panels: Vacuum pumps are utilized in the manufacturing of vacuum insulation panels, which offer superior insulation properties for buildings and appliances.
6. Power Generation:
Vacuum pumps play a role in power generation applications:
– Steam Condenser Systems: Vacuum pumps are used in power plants to remove non-condensable gases from steam condenser systems, improving thermal efficiency.
– Gas Capture: Vacuum pumps are utilized to capture and remove gases, such as hydrogen or helium, in nuclear power plants, research reactors, or particle accelerators.
These are just a few examples of the primary applications of vacuum pumps. The versatility and wide range of vacuum pump types make them essential in numerous industries, contributing to various manufacturing processes, research endeavors, and technological advancements.


editor by Dream 2024-05-15
China Good quality Oil Free Dry Screw CHINAMFG Electric Brake High Vacuum Pump vacuum pump connector
Product Description
Oil Free Dry Screw CHINAMFG Electric Brake High Vacuum Pump
Product Description
The LGB screw vacuum pump is an extraction equipment that uses a pair of screws to perform synchronous high-speed reverse rotation in the pump casing, generating suction and exhaust effects. Due to the certain gap between the screws, the pump operates smoothly without friction, with low noise, and no need for lubricating oil in the working chamber. Therefore, the dry screw pump can extract gas containing water vapor and a small amount of dust; Due to the maximum pressure of the LGB screw vacuum pump CHINAMFG 5PA, it can be widely used in various fields such as chemical industry, metallurgy, electronics, petroleum, aerospace, tools, papermaking, packaging, food, medicine, medical equipment, as well as information engineering, biotechnology, microelectronics, etc
Product Parameters
|
Model |
LGB-70 |
LGB-100 |
LGB-200 |
LGB-300 |
|
Pumping speed(L/3) |
70 |
100 |
200 |
300 |
|
Ultimate pressure(Pa) |
5 |
5 |
5 |
5 |
|
rotational speed(rpm) |
2900 |
2940 |
2940 |
2950 |
|
Connections of inlet DN(mm) |
50 |
80 |
100 |
125 |
|
Connections of outle DN(mm) |
45 |
65 |
65 |
80 |
|
Noise level dB(A) |
≤80 |
≤80 |
≤80 |
≤80 |
|
temperature rise(°C) |
≤40°C |
≤40°C |
≤40°C |
≤40°C |
|
Pumping size(mm) |
1360X960X700 |
1650X847X933 |
1740X960X980 |
2100X1100X1030 |
|
Weight (with oil filling) kg |
500 |
665 |
1571 |
1300 |
|
Motor Power(Kw) |
7.5 |
15 |
18.5 |
37 |
|
Motor Voltage/motor base frequency(V/Hz) |
380/50 |
380/50 |
380/50 |
380/50 |
|
Nominal Motor speed (rpm) |
2900 |
2940 |
2940 |
2950 |
|
Nominal Motor current(A) |
14.8 |
28.8 |
35.5 |
67.9 |
|
Type of protection(IP) |
IP55 |
IP55 |
IP55 |
IP55 |
Detailed Photos
Choose the right materials and weld carefully
Surface texture, smooth lines, good quality visible
Performance stability and outstanding advantages
We can recommend the closest model according to your requirements
Long term use and high efficiency
Compact structure, low noise, and reliable use
Easy to disassemble and maintain
Can be selected according to process requirements
Materials and sealing methods for the overcurrent section of the pump
Company Profile
HangZhou Sifang Vacuum Equipment Co., Ltd. specializes in the production of vacuum furnaces, vacuum pumps, steel drums and other products.”Sifang” is the registered trademark of the company’s products.
our company is 1 professional vacuum equipment manufacturer in HangZhou, China. We specialize in vacuum pumps, furnaces, systems and components for diverse applications. We produce rotary vane vacuum pumps, water ring vacuum pumps, reciprocating vacuum pumps, roots vacuum pump units, vacuum heat treatment furnaces, vacuum aluminum brazing furnaces, high temperature brazing fur- naces, vacuum sintering furnaces, monocrystalline silicon furnaces and other products. All these vacuum equipment are widely used in aviation, aerospace, military, railway, automobile, machinery, mold, electronics, metallurgy, scientific research and other fields.
We have professional engineer support, high efficiency sales team and competitive price superiority, and attract customers from all over the world, we export to over 40 countries, including Europe, Poland, Serbia, Turkey, Russia, USA, Mexico, Brazil, India, Thailand, Middle east and South Africa.
After several years’ development, We have achieved great progress, we are equipped with the AutomaticCNCmachines and multi-func- tion testing machines. Our R&D department provide the strong tech- nical support and enable us to receive some 0 E M, O D M projects. We can produce at least 3000 sets vacuum equipment per year. With our innovative and energy-efficient vacuum equipment that is put to work in a multitude of manufacturing and process applica- tions, we also offer you a comprehensive suite of CHINAMFG ser- vices to complement our products.
FAQ
1.Q: Are you a factory or trading company?
A: We are a factory and we have professional team of workers,Designers and inspectors.
2.Q:Do you accept custom?
A:Of course.We have professional teams who make your designs,photos,imagines and OEM orders into real production.
3.Q:What’s your advantages?
A: Quick response to your enquiry,
High quality control,
Reasonable price,
Timely delivery,
Excellent after-sales service,
OEM/ODM are welcome
4.Q:What’s your shipping terms?
A:If you need to ship by air,we can use DHL,UPS,FedEx,TNT or EMS.If you need to ship by sea,we have many good forwarders to work with,they can provide the best price for you.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | Online Support |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 1 Year |
| Oil or Not: | Oil |
| Structure: | Vacuum Pump |
| Exhauster Method: | Entrapment Vacuum Pump |
| Vacuum Degree: | Vacuum |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
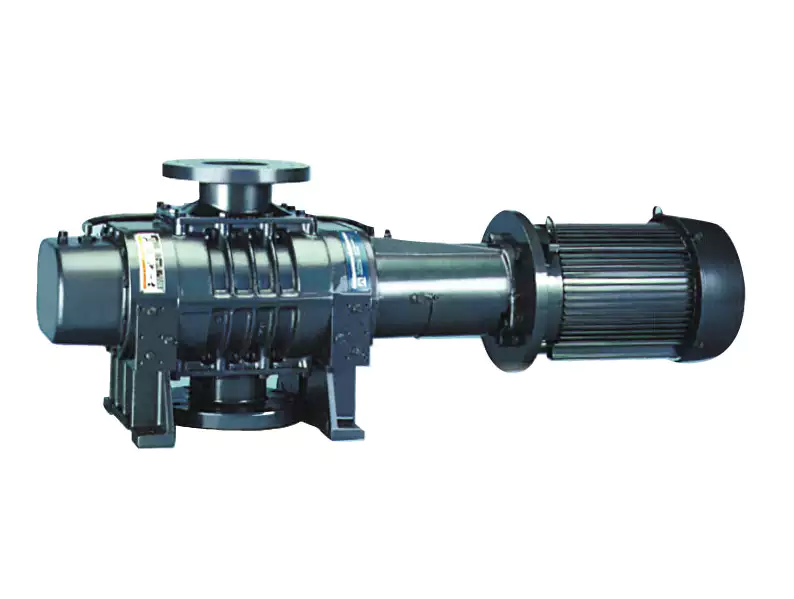

What Is the Role of Vacuum Pumps in Semiconductor Manufacturing?
Vacuum pumps play a critical role in semiconductor manufacturing processes. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Semiconductor manufacturing involves the production of integrated circuits (ICs) and other semiconductor devices used in various electronic applications. Vacuum pumps are used extensively throughout the semiconductor manufacturing process to create and maintain the required vacuum conditions for specific manufacturing steps.
Here are some key roles of vacuum pumps in semiconductor manufacturing:
1. Deposition Processes: Vacuum pumps are used in deposition processes such as physical vapor deposition (PVD) and chemical vapor deposition (CVD). These processes involve depositing thin films of materials onto semiconductor wafers to create various layers and patterns. Vacuum pumps help create a low-pressure environment necessary for precise control of the deposition process, ensuring uniform and high-quality film formation.
2. Etching and Cleaning: Vacuum pumps are utilized in etching and cleaning processes, which involve the removal of specific layers or contaminants from semiconductor wafers. Dry etching techniques, such as plasma etching and reactive ion etching, require a vacuum environment to facilitate the ionization and removal of material. Vacuum pumps aid in creating the necessary low-pressure conditions for efficient etching and cleaning processes.
3. Ion Implantation: Ion implantation is a process used to introduce impurities into specific regions of a semiconductor wafer to modify its electrical properties. Vacuum pumps are used to evacuate the ion implantation chamber, creating the required vacuum environment for accurate and controlled ion beam acceleration and implantation.
4. Wafer Handling and Transfer: Vacuum pumps are employed in wafer handling and transfer systems. These systems utilize vacuum suction to securely hold and manipulate semiconductor wafers during various manufacturing steps, such as loading and unloading from process chambers, robotic transfer between tools, and wafer alignment.
5. Load Lock Systems: Load lock systems are used to transfer semiconductor wafers between atmospheric conditions and the vacuum environment of process chambers. Vacuum pumps are integral components of load lock systems, creating and maintaining the vacuum conditions necessary for wafer transfer while minimizing contamination risks.
6. Metrology and Inspection: Vacuum pumps are utilized in metrology and inspection tools used for characterizing semiconductor devices. These tools, such as scanning electron microscopes (SEMs) and focused ion beam (FIB) systems, often operate in a vacuum environment to enable high-resolution imaging and accurate analysis of semiconductor structures and defects.
7. Leak Detection: Vacuum pumps are employed in leak detection systems to identify and locate leaks in vacuum chambers, process lines, and other components. These systems rely on vacuum pumps to evacuate the system and then monitor for any pressure rise, indicating the presence of leaks.
8. Cleanroom Environment Control: Semiconductor manufacturing facilities maintain cleanroom environments to prevent contamination during the fabrication process. Vacuum pumps are used in the design and operation of the cleanroom ventilation and filtration systems, helping to maintain the required air cleanliness levels by removing particulates and maintaining controlled air pressure differentials.
Vacuum pumps used in semiconductor manufacturing processes are often specialized to meet the stringent requirements of the industry. They need to provide high vacuum levels, precise control, low contamination levels, and reliability for continuous operation.
Overall, vacuum pumps are indispensable in semiconductor manufacturing, enabling the creation of the necessary vacuum conditions for various processes, ensuring the production of high-quality semiconductor devices.
How Do Vacuum Pumps Impact the Quality of 3D Printing?
Vacuum pumps play a significant role in improving the quality and performance of 3D printing processes. Here’s a detailed explanation:
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a process of creating three-dimensional objects by depositing successive layers of material. Vacuum pumps are utilized in various aspects of 3D printing to enhance the overall quality, accuracy, and reliability of printed parts. Here are some key ways in which vacuum pumps impact 3D printing:
1. Material Handling and Filtration: Vacuum pumps are used in 3D printing systems to handle and control the flow of materials. They create the necessary suction force to transport powdered materials, such as polymers or metal powders, from storage containers to the printing chamber. Vacuum systems also assist in filtering and removing unwanted particles or impurities from the material, ensuring the purity and consistency of the feedstock. This helps to prevent clogging or contamination issues during the printing process.
2. Build Plate Adhesion: Proper adhesion of the printed object to the build plate is crucial for achieving dimensional accuracy and preventing warping or detachment during the printing process. Vacuum pumps are employed to create a vacuum environment or suction force that securely holds the build plate and ensures firm adhesion between the first layer of the printed object and the build surface. This promotes stability and minimizes the risk of layer shifting or deformation during the printing process.
3. Material Drying: Many 3D printing materials, such as filament or powdered polymers, can absorb moisture from the surrounding environment. Moisture-contaminated materials can lead to poor print quality, reduced mechanical properties, or defects in the printed parts. Vacuum pumps with integrated drying capabilities can be employed to create a low-pressure environment, effectively removing moisture from the materials before they are used in the printing process. This ensures the dryness and quality of the materials, resulting in improved print outcomes.
4. Resin Handling in Stereolithography (SLA): In SLA 3D printing, a liquid resin is selectively cured using light sources to create the desired object. Vacuum pumps are utilized to facilitate the resin handling process. They can be employed to degas or remove air bubbles from the liquid resin, ensuring a smooth and bubble-free flow during material dispensing. This helps to prevent defects and imperfections caused by trapped air or bubbles in the final printed part.
5. Enclosure Pressure Control: Some 3D printing processes, such as selective laser sintering (SLS) or binder jetting, require the printing chamber to be maintained at a specific pressure or controlled atmosphere. Vacuum pumps are used to create a controlled low-pressure or vacuum environment within the printing chamber, enabling precise pressure regulation and maintaining the desired conditions for optimal printing results. This control over the printing environment helps to prevent oxidation, improve material flow, and enhance the quality and consistency of printed parts.
6. Post-Processing and Cleaning: Vacuum pumps can also aid in post-processing steps and cleaning of 3D printed parts. For instance, in processes like support material removal or surface finishing, vacuum systems can assist in the removal of residual support structures or excess powder from printed objects. They can also be employed in vacuum-based cleaning methods, such as vapor smoothing, to achieve smoother surface finishes and enhance the aesthetics of the printed parts.
7. System Maintenance and Filtration: Vacuum pumps used in 3D printing systems require regular maintenance and proper filtration to ensure their efficient and reliable operation. Effective filtration systems within the vacuum pumps help to remove any contaminants or particles generated during printing, preventing their circulation and potential deposition on the printed parts. This helps to maintain the cleanliness of the printing environment and minimize the risk of defects or impurities in the final printed objects.
In summary, vacuum pumps have a significant impact on the quality of 3D printing. They contribute to material handling and filtration, build plate adhesion, material drying, resin handling in SLA, enclosure pressure control, post-processing and cleaning, as well as system maintenance and filtration. By utilizing vacuum pumps in these critical areas, 3D printing processes can achieve improved accuracy, dimensional stability, material quality, and overall print quality.
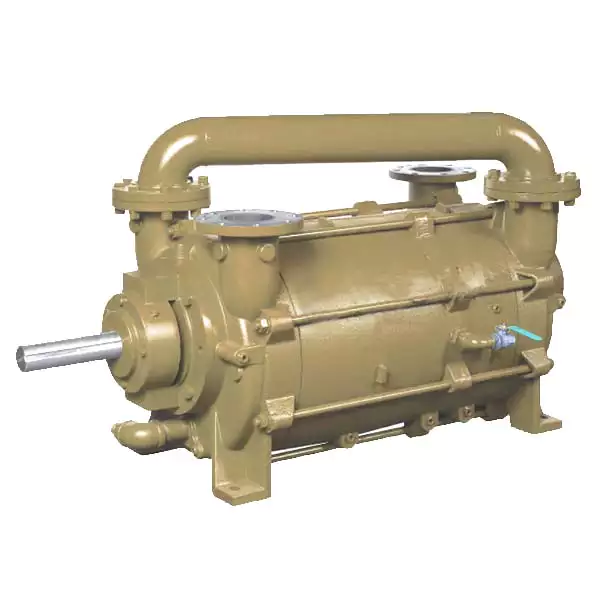

What Is a Vacuum Pump, and How Does It Work?
A vacuum pump is a mechanical device used to create and maintain a vacuum or low-pressure environment within a closed system. Here’s a detailed explanation:
A vacuum pump operates on the principle of removing gas molecules from a sealed chamber, reducing the pressure inside the chamber to create a vacuum. The pump accomplishes this through various mechanisms and techniques, depending on the specific type of vacuum pump. Here are the basic steps involved in the operation of a vacuum pump:
1. Sealed Chamber:
The vacuum pump is connected to a sealed chamber or system from which air or gas molecules need to be evacuated. The chamber can be a container, a pipeline, or any other enclosed space.
2. Inlet and Outlet:
The vacuum pump has an inlet and an outlet. The inlet is connected to the sealed chamber, while the outlet may be vented to the atmosphere or connected to a collection system to capture or release the evacuated gas.
3. Mechanical Action:
The vacuum pump creates a mechanical action that removes gas molecules from the chamber. Different types of vacuum pumps use various mechanisms for this purpose:
– Positive Displacement Pumps: These pumps physically trap gas molecules and remove them from the chamber. Examples include rotary vane pumps, piston pumps, and diaphragm pumps.
– Momentum Transfer Pumps: These pumps use high-speed jets or rotating blades to transfer momentum to gas molecules, pushing them out of the chamber. Examples include turbomolecular pumps and diffusion pumps.
– Entrapment Pumps: These pumps capture gas molecules by adsorbing or condensing them on surfaces or in materials within the pump. Cryogenic pumps and ion pumps are examples of entrainment pumps.
4. Gas Evacuation:
As the vacuum pump operates, it creates a pressure differential between the chamber and the pump. This pressure differential causes gas molecules to move from the chamber to the pump’s inlet.
5. Exhaust or Collection:
Once the gas molecules are removed from the chamber, they are either exhausted into the atmosphere or collected and processed further, depending on the specific application.
6. Pressure Control:
Vacuum pumps often incorporate pressure control mechanisms to maintain the desired level of vacuum within the chamber. These mechanisms can include valves, regulators, or feedback systems that adjust the pump’s operation to achieve the desired pressure range.
7. Monitoring and Safety:
Vacuum pump systems may include sensors, gauges, or indicators to monitor the pressure levels, temperature, or other parameters. Safety features such as pressure relief valves or interlocks may also be included to protect the system and operators from overpressure or other hazardous conditions.
It’s important to note that different types of vacuum pumps have varying levels of vacuum they can achieve and are suitable for different pressure ranges and applications. The choice of vacuum pump depends on factors such as the required vacuum level, gas composition, pumping speed, and the specific application’s requirements.
In summary, a vacuum pump is a device that removes gas molecules from a sealed chamber, creating a vacuum or low-pressure environment. The pump accomplishes this through mechanical actions, such as positive displacement, momentum transfer, or entrapment. By creating a pressure differential, the pump evacuates gas from the chamber, and the gas is either exhausted or collected. Vacuum pumps play a crucial role in various industries, including manufacturing, research, and scientific applications.


editor by Dream 2024-05-10
China Good quality CZPT Small High Performance High Pressure Diaphragm DC Air Pump, Mini Membrane Brush DC Vacuum Pump vacuum pump connector
Product Description
Topsflo Small High Performance High Pressure Diaphragm DC Air Pump, Mini Membrane Brush DC Vacuum Pump
Description:
CZPT micro diaphragm pumps and compressors are based on a simple principal, the circular power from the motor is converted into oscillating movement by an eccentric, which moves up and down its central point, this motion is then transferred to a diaphragm by means of a connecting rod, an elastic diaphragm, which in conjunction with an inlet and outlet valve creates a pumping action.
The TM 40 Series offers multiple component configurations allowing them to be used for either vacuum operation, pressure operation, or alternating vacuum and pressure operations.The innovative, compact design incorporates leading edge technologies that allow it to operate harder, quieter and longer, reliabler, highly efficient.
TM 40 pumps can be mounted in any position and can deliver up to 13 l/min, 16L/min (dual head) depending on the model and will operate against pressures of up to 280Kpa.
Specification:
| Model |
Pressure Pump | Vacuum Pump | Rated Voltage | No-load Current | Max Pressure | Max Vacuum | Max Flow |
| (Item Number) | (Item Number) | (Vdc) | (A) | (KPa) | (KPa) | (L/min) | |
| TM40-B | TM40A-B01-12-P22013 | TM40A-B01-12-V8013 | 12 | 0.7 | 220 | -80 | 13 |
| TM40-B02-12-P28016 | TM40A-B02-12-V8016 | 12 | 1.2 | 280 | -80 | 16 | |
| ” P ” means pressure pump, ” V ” means vacuum pump, “12/24” means different voltages optional. | |||||||
| Pump Weight:280g; Pump Size:86*mm*65mm*40.5mm; Inlet&Outlet:OD 6.5mm/ID 3.4mm,hose suggestion:ID 5.0mm | |||||||
| Materials:pump head Nylon, membrane EPDM, valve EPDM Motor type and code:”B”means economical brush DC motor (reference lifetime ≥1,000hours) |
|||||||
Features:
Highest Performance/Size Ratio
Innovative and efficient engineering designs enable the TM 40 Series to push the performance envelope in a lightweight, compact size.
Performs Quieter
Optimized head, chamber, and flow path reduce noise without compromising performance.
Lasts Reliably Longer
Uncontaminated flow
no contamination of the media due to oil-free operation
Little vibration
Because of leading edge technologies, top quality bearing, superior brushless motor
High level of gas tightness
thanks to stress-optimised structured diaphragm, newly-designed valves and sealing systems, precise placement of the pump head
Extreme chemical resistance
The use of chemically resistant materials optional such as PTFE FKM or other ,material combinations for the parts which allows the corrosive gas to be pumped.
Optimal solution for your application
a wide standard range of materials, motors , voltages configurates multiple components system selected
Typical Application:
Industrial pressure and vacuum applications
Portable Analytical Instruments
Medical Diagnostic Equipment
Air Quality Sampling Monitors
Respiration Monitors
Gas or Odor Leak Detectors
Dimension(mm) & Curve:
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Material: | Head Nylon, Membrane EPDM / PTFE, Valve EPDM / FPM |
|---|---|
| Power: | Electric |
| Function: | Electronic Type |
| Motor: | DC Brush,Motor |
| Materials: | Pump Head Nylon, Membrane EPDM / PTFE, Valve EPDM |
| Life-Time: | 1200hour |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

How to check the vacuum pump
A vacuum pump is a machine that draws gas molecules from a volume and maintains a partial vacuum. Its main job is to create a relative vacuum within the stated capabilities. If your vacuum pump isn’t working properly, it may need service. Read on to learn more about the types of vacuum pumps and how to check them.
Principle of industrial vacuum pump
Industrial vacuum pumps are used in industrial processes that require vacuum. These pumps are designed to generate, improve and maintain vacuum. Learn about the different types of industrial vacuum technology. You can start by reading about the most common types of industrial vacuum pumps. These pumps can be used in a variety of industrial processes from cleaning to manufacturing.
Regardless of the technology used to manufacture these pumps, the basic principles behind their operation are the same. The speed and mass flow of the pump will determine its capacity and suitability. A faster flow rate will minimize the time it takes for the machine to empty. Another important factor to consider is the type of vacuum you need.
A liquid ring vacuum pump is an industrial pump that uses a ring of liquid to form a seal. This type of pump is best suited for applications with high vapor loads and high liquid carry-over. Liquid ring vacuum pumps can be divided into two categories: liquid ring vacuum pumps and scroll vacuum pumps.
Industrial vacuum pumps work by removing gas molecules from a chamber. The partial vacuum created allows material to flow through the void. As more molecules are removed, the pressure in the chamber decreases, releasing energy that can be used for a variety of different purposes.
The most common use of industrial vacuum pumps is for electric lights. In these lamps, a vacuum pump removes the gas, causing the bulb to light up. Energy from the vacuum is also used in aircraft to power instruments. In addition to powering industrial vacuum cleaners, they are used in a variety of other environments.
High-performance industrial vacuum systems require specific materials that can withstand extreme pressure. This means that the materials used in these systems need to be properly checked. They must also be free of organic debris and other contaminants before they can be safely placed in the chamber.
Types of vacuum pumps
There are various types of vacuum pumps. Which one to choose should depend on the purpose of the pump and the degree of vacuum that must be achieved. It is mainly divided into three categories: rough vacuum or low vacuum, high vacuum and ultra-high vacuum. They all have varying degrees of scarcity. The higher the pressure, the fewer molecules per cubic centimeter. This in turn improves vacuum quality.
The vacuum pump is critical to the operation of the vacuum system. These devices are divided into three main categories according to their working pressure range. These pumps have different characteristics and technologies that make them ideal for specific applications. The choice of vacuum pump required for a particular application depends on how much vacuum you need, and how much power you are willing to spend.
Vacuum pumps are used in a variety of industrial and scientific processes. Their main function is to remove gas molecules from the sealed volume, leaving a partial vacuum. There are many different types of vacuum pumps, including rotary piston, liquid ring and scroll vacuum pumps. In addition, turbomolecular pumps are used.
Dry vacuum pumps are more expensive than wet vacuum pumps. Wet vacuum pumps use oil as their lubricating fluid. Different types of oils are used depending on the application. Some wet pumps have additional features, including contaminant filtration. However, wet systems have one major disadvantage: the contact between oil and fluid. To avoid this, oil separators are usually used.
There are several different types of vacuum pumps. The basic type is the positive displacement pump. It operates by expanding the chamber and removing gas molecules. The intake valve draws fluid into the chamber, while the exhaust valve opens when the chamber is at maximum expansion. This cycle repeats several times per second. Positive displacement pumps are often used in multistage vacuum systems. 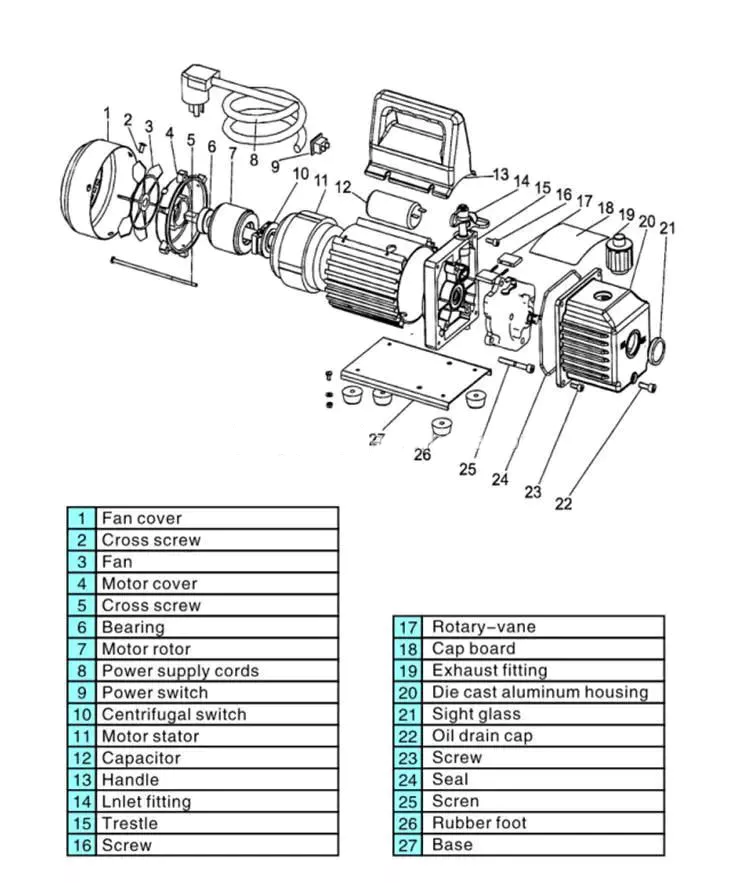
Maintenance of vacuum pump
Regular maintenance is very important to ensure the long-term effective use of the vacuum pump. One way to ensure proper pump performance is to change the oil regularly. Pump oil may be contaminated by vapor condensation. To avoid this problem, close the inlet valve for 20 to 30 minutes before applying vacuum. It is also important to install an inlet cold trap to protect the pump from corrosive vapors.
Another way to prolong the life of your vacuum pump is to periodically remove any solvent in it. This step reduces internal corrosion and prevents premature pump failure. During maintenance, be sure to disconnect the power supply to the vacuum pump. After cleaning, store it in a dry and safe place. The pump should also be disposed of in accordance with local regulations.
Vacuum pumps may require frequent oil changes, especially when used in wet chemistry. The standard rule is to change the oil after 3,000 hours of use, but some pumps require more frequent oil changes. It is also important to clean the oil regularly, as dirty or discolored oil can affect the performance of the pump.
Vacuum pumps are often equipped with on-site glass to allow the user to visually check the oil level. Clean oil will appear transparent, while dirty oil will appear darker. Frequent oil changes are essential, as oil changes can help spot various potential problems. Changes in vacuum pump performance or strange noises are also good indicators of a problem.
After an oil change, the vacuum pump should be cleaned thoroughly with a soft cloth and mild degreaser. Oil changes should take less than ten minutes, and they will extend the life of your equipment. Additionally, the outside of the pump should be wiped with a cloth or rag.
The pump must be properly vented to avoid internal corrosion. If possible, place the pump away from hot equipment or rooms. Overheating can reduce the viscosity of the oil and cause premature pump failure. In addition, it can lead to overwork of other expensive scientific equipment. Heat can also cause cracked rubber parts and oil leaks. 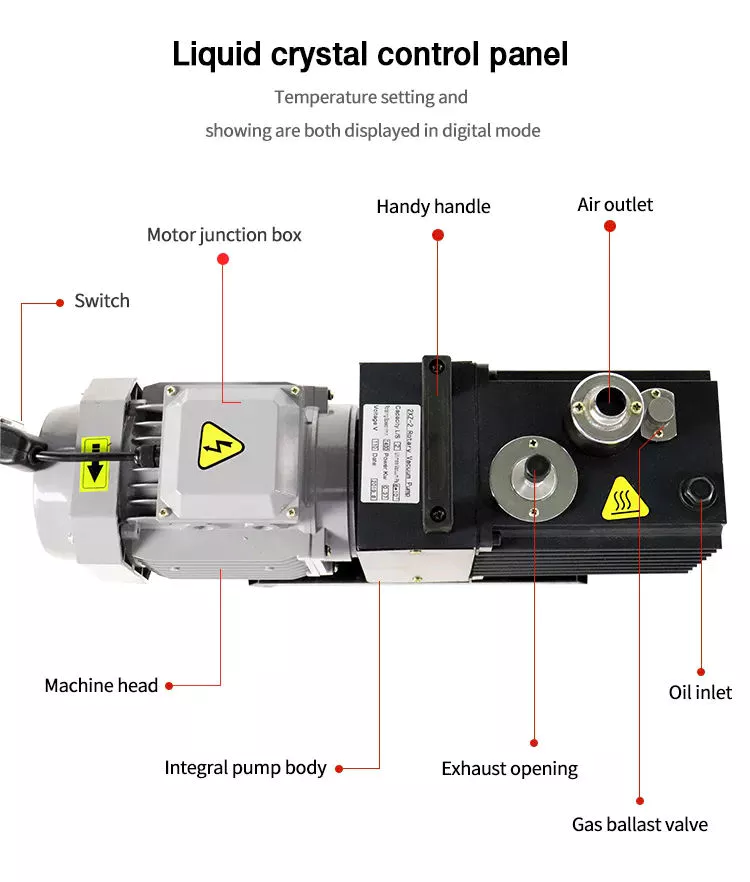
Signs of damage to the vacuum pump
A bad vacuum pump can cause a variety of automotive problems, including poor fuel economy, difficult braking, undercarriage oil leaks, and faulty air conditioning. If any of these problems occur, call a mechanic to check your vehicle’s vacuum pump. You can also check the air conditioner and brake pedal to see if they are working properly.
A loud noise from the pump can also be a symptom of a malfunction. These noises are often caused by the aging and accumulated wear of specific components. If this is the case, the diaphragm, valve plate or seals may need to be replaced. However, if the noise is coming from bearings or other areas, more extensive repairs may be required. Additionally, dust and other contaminants can enter the pump chamber, which can degrade pump performance.
If the vacuum pump won’t start, it could be a blown fuse or a power or voltage problem. Other common causes are flow restrictions or improper installation at the entrance. Also, the vacuum pump may be damaged or the capacitors may be of poor quality. It’s not always easy to tell if a vacuum pump is leaking oil, but a greasy transmission can indicate a vacuum pump failure.
A leaking vacuum pump can also hiss when the car’s engine is running. If you hear it, check the hoses and connections to make sure there are no leaks. A vacuum leak may indicate a faulty vacuum pump, so you need to replace it as soon as possible.
Checking end pressure is easy, but a pressure gauge can also serve as a sign. You can also check for pump vibration by running a short procedure. Excessive vibration can be subtle, but it can greatly affect your process. If you notice excessive pump vibration, you should contact a professional immediately.
Poor pump performance can cause many problems for your company. A bad vacuum pump not only wastes material, it also damages your tools and reputation.


editor by Dream 2024-05-09
China supplier 11HP High Efficiency Waste Collection Industrial Vacuum Pump for CNC Router Machine with Good quality
Product Description
Product Parameters
| Product Name | 11HP High Efficiency Waste Collection Industrial Vacuum Pump for CNC Router Machine | |
| Model No. | GHBH 011 36 1R9 | |
| Frequency | 50Hz | 60Hz |
| Rated Power | 8.5kW | 9.8kW |
| Rated Voltage | 345-415△/600-690Y(V) | 380-480△/660-720Y(V) |
| Rated Current | 18.2△/10.5Y(A) | 18.2△/10.5Y(A) |
| Max Airflow | 1050m³/h | 1250m³/h |
| Max Vacuum | -190mbar | -150mbar |
| Max Pressure | 190mbar | 140mbar |
| Sound | 74db(A) | 79db(A) |
| Weight | 93kg | 93kg |
Product Features
GOORUI Side channel blowers are maintenance-free:
·External, permanently lubricated bearings
·Contactless rotating impellers
·Fan-cooled motors
GOORUI Side channel blowers are user-friendly:
·Weight-optimised design through aluminum pressure casting parts
·Possibility for a vertical or horizontal installation
·Suitability for converter operation
GOORUI Side channel blowers are environmentally friendly:
·Oil-free operation
·Low energy requirement
·Low noise emission
GOORUI Side channel blowers can be used world-wide:
·50/60Hz voltage range motors of the Iso class F
·Protection type IP55 with an integrated thermal protection switch (standard)
·CE, TUV, RoHS, CCC and ISO9001 certifications
Performance Curves
Dimensions
Application
GOORUI Side Channel Blower Applications For CNC Router Machine
Accessories
We also have some parts for your application, if you need, welcome to tell me.
Air filter: Filter the dust particles, apply to a bad environment.
Silencer: reduce blower noise 5-10db, apply to a quiet environment.
Pressure relief valve: Control gas pressure, prevent excessive pressure, damage the machine.
Installation Instructions
Instructions:
1. It should be placed in a relatively stable place, and the surrounding environment should be clean, dry and ventilated.
2. The direction of rotation of the impeller must be consistent with the direction of the pointed tip marked on the fan cover.
3. When working, the working pressure should not be greater than 8 kPa, so as to avoid excessive heat generation of the air pump and damage to the air pump caused by motor overcurrent.
4. It is strictly forbidden for solid, liquid and corrosive gas to enter the pump body.
5. The filters and silencers at both ends of the air inlet and outlet should be cleaned in time according to the situation to avoid clogging and affecting use.
6. The external connection of the air inlet and outlet must be connected by a hose (rubber tube, plastic spring tube).
Precautions:
1. Flat washers and spring washers must be used to tighten the screws.
2. It is best to use rubber buffer rubber to bear the weight of the vortex air pump, especially the high-power vortex air pump, which is indispensable.
3. For some occasions that require noise, a silencer can be installed to reduce the noise (generally down, about 5 dB), the silencer is installed at the end of the inlet duct or outlet duct.
4. For some occasions with high requirements for noise, you can add a layer of silencer cotton according to the conditions of the machine itself to meet the noise requirements on site. For details, please consult our customer service.
5. When using silencing cotton to silence the sound, pay attention to the distance between the vortex air pump and the box, pay attention to the ventilation and heat dissipation of the vortex air pump, and pay attention to using rubber cushioning to bear the weight of the vortex air pump. According to the picture, you need to consult customer service.
6. The air inlet and outlet of the vortex air pump For pipe connection, hose connection should be used to isolate vibration.
Packaging & Shipping
| Shipping way: By sea or By air or By your agent in China. | |
| Delivery terms | Delivery time |
| CIF by sea or air freight terms FOB HangZhou/HangZhou EX-WORK TERMS DDP/DDU DHL/FEDEX/UPS courier door to door Other delivery terms are negotiable. |
In stock blower: 2-3 days after payment Out of stock blower: 7-15 days after order confirmed. Special blower need to check specific |
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Material: | Aluminum |
|---|---|
| Usage: | for CNC Router Machine |
| Flow Direction: | Side Channel |
| Pressure: | High Pressure |
| Certification: | RoHS, ISO, CE, CCC |
| Color: | Silver/Golden |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
What Are the Advantages of Using Oil-Sealed Vacuum Pumps?
Oil-sealed vacuum pumps offer several advantages in various applications. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. High Vacuum Performance: Oil-sealed vacuum pumps are known for their ability to achieve high levels of vacuum. They can create and maintain deep vacuum levels, making them suitable for applications that require a low-pressure environment. The use of oil as a sealing and lubricating medium helps in achieving efficient vacuum performance.
2. Wide Operating Range: Oil-sealed vacuum pumps have a wide operating range, allowing them to handle a broad spectrum of vacuum levels. They can operate effectively in both low-pressure and high-vacuum conditions, making them versatile for different applications across various industries.
3. Efficient and Reliable Operation: These pumps are known for their reliability and consistent performance. The oil-sealed design provides effective sealing, preventing air leakage and maintaining a stable vacuum level. They are designed to operate continuously for extended periods without significant performance degradation, making them suitable for continuous industrial processes.
4. Contamination Handling: Oil-sealed vacuum pumps are effective in handling certain types of contaminants that may be present in the process gases or air being evacuated. The oil acts as a barrier, trapping and absorbing certain particulates, moisture, and chemical vapors, preventing them from reaching the pump mechanism. This helps protect the pump internals from potential damage and contributes to the longevity of the pump.
5. Thermal Stability: The presence of oil in these pumps helps in dissipating heat generated during operation, contributing to their thermal stability. The oil absorbs and carries away heat, preventing excessive temperature rise within the pump. This thermal stability allows for consistent performance even during prolonged operation and helps protect the pump from overheating.
6. Noise Reduction: Oil-sealed vacuum pumps generally operate at lower noise levels compared to other types of vacuum pumps. The oil acts as a noise-damping medium, reducing the noise generated by the moving parts and the interaction of gases within the pump. This makes them suitable for applications where noise reduction is desired, such as laboratory environments or noise-sensitive industrial settings.
7. Versatility: Oil-sealed vacuum pumps are versatile and can handle a wide range of gases and vapors. They can effectively handle both condensable and non-condensable gases, making them suitable for diverse applications in industries such as chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, food processing, and research laboratories.
8. Cost-Effective: Oil-sealed vacuum pumps are often considered cost-effective options for many applications. They generally have a lower initial cost compared to some other types of high-vacuum pumps. Additionally, the maintenance and operating costs are relatively lower, making them an economical choice for industries that require reliable vacuum performance.
9. Simplicity and Ease of Maintenance: Oil-sealed vacuum pumps are relatively simple in design and easy to maintain. Routine maintenance typically involves monitoring oil levels, changing the oil periodically, and inspecting and replacing worn-out parts as necessary. The simplicity of maintenance procedures contributes to the overall cost-effectiveness and ease of operation.
10. Compatibility with Other Equipment: Oil-sealed vacuum pumps are compatible with various process equipment and systems. They can be easily integrated into existing setups or used in conjunction with other vacuum-related equipment, such as vacuum chambers, distillation systems, or industrial process equipment.
These advantages make oil-sealed vacuum pumps a popular choice in many industries where reliable, high-performance vacuum systems are required. However, it’s important to consider specific application requirements and consult with experts to determine the most suitable type of vacuum pump for a particular use case.

How Do Vacuum Pumps Assist in Freeze-Drying Processes?
Freeze-drying, also known as lyophilization, is a dehydration technique used in various industries, including pharmaceutical manufacturing. Vacuum pumps play a crucial role in facilitating freeze-drying processes. Here’s a detailed explanation:
During freeze-drying, vacuum pumps assist in the removal of water or solvents from pharmaceutical products while preserving their structure and integrity. The freeze-drying process involves three main stages: freezing, primary drying (sublimation), and secondary drying (desorption).
1. Freezing: In the first stage, the pharmaceutical product is frozen to a solid state. Freezing is typically achieved by lowering the temperature of the product below its freezing point. The frozen product is then placed in a vacuum chamber.
2. Primary Drying (Sublimation): Once the product is frozen, the vacuum pump creates a low-pressure environment within the chamber. By reducing the pressure, the boiling point of water or solvents present in the frozen product is lowered, allowing them to transition directly from the solid phase to the vapor phase through a process called sublimation. Sublimation bypasses the liquid phase, preventing potential damage to the product’s structure.
The vacuum pump maintains a low-pressure environment by continuously removing the water vapor or solvent vapor generated during sublimation. The vapor is drawn out of the chamber, leaving behind the freeze-dried product. This process preserves the product’s original form, texture, and biological activity.
3. Secondary Drying (Desorption): After the majority of the water or solvents have been removed through sublimation, the freeze-dried product may still contain residual moisture or solvents. In the secondary drying stage, the vacuum pump continues to apply vacuum to the chamber, but at a higher temperature. The purpose of this stage is to remove the remaining moisture or solvents through evaporation.
The vacuum pump maintains the low-pressure environment, allowing the residual moisture or solvents to evaporate at a lower temperature than under atmospheric pressure. This prevents potential thermal degradation of the product. Secondary drying further enhances the stability and shelf life of the freeze-dried pharmaceutical product.
By creating and maintaining a low-pressure environment, vacuum pumps enable efficient and controlled sublimation and desorption during the freeze-drying process. They facilitate the removal of water or solvents while minimizing the potential damage to the product’s structure and preserving its quality. Vacuum pumps also contribute to the overall speed and efficiency of the freeze-drying process by continuously removing the vapor generated during sublimation and evaporation. The precise control provided by vacuum pumps ensures the production of stable and high-quality freeze-dried pharmaceutical products.

What Industries Commonly Rely on Vacuum Pump Technology?
Vacuum pump technology finds applications in various industries where creating and controlling vacuum or low-pressure environments is crucial. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Manufacturing and Production: Vacuum pumps are extensively used in manufacturing and production processes across multiple industries. They are employed for tasks such as vacuum molding, vacuum packaging, vacuum degassing, vacuum drying, and vacuum distillation. Industries like automotive, aerospace, electronics, pharmaceuticals, and food processing rely on vacuum pump technology to achieve precise and controlled manufacturing conditions.
2. Chemical and Pharmaceutical: The chemical and pharmaceutical industries heavily rely on vacuum pumps for numerous applications. These include solvent recovery, vacuum filtration, vacuum drying, distillation, crystallization, and evaporation. Vacuum pumps enable these industries to carry out critical processes under reduced pressure, ensuring efficient separation, purification, and synthesis of various chemical compounds and pharmaceutical products.
3. Semiconductor and Electronics: The semiconductor and electronics industries extensively use vacuum pumps for manufacturing microchips, electronic components, and electronic devices. Vacuum pumps are crucial in processes such as physical vapor deposition (PVD), chemical vapor deposition (CVD), etching, ion implantation, and sputtering. These processes require controlled vacuum conditions to ensure precise deposition, surface modification, and contamination-free manufacturing.
4. Research and Development: Vacuum pump technology is integral to research and development activities across scientific disciplines. It supports experiments and investigations in fields such as physics, chemistry, materials science, biology, and environmental science. Vacuum pumps facilitate processes like freeze drying, vacuum distillation, vacuum evaporation, vacuum spectroscopy, and creating controlled atmospheric conditions for studying various phenomena.
5. Food and Beverage: The food and beverage industry relies on vacuum pumps for packaging and preservation purposes. Vacuum sealing is used to extend the shelf life of food products by removing air and creating a vacuum-sealed environment that inhibits spoilage and maintains freshness. Vacuum pumps are also used in processes like freeze drying, vacuum concentration, and vacuum cooling.
6. Oil and Gas: In the oil and gas industry, vacuum pumps play a role in various applications. They are used for crude oil vacuum distillation, vacuum drying, vapor recovery, gas compression, and gas stripping processes. Vacuum pumps help maintain optimal conditions during oil refining, gas processing, and petrochemical manufacturing.
7. Environmental and Waste Management: Vacuum pumps are employed in environmental and waste management applications. They are used for tasks such as soil vapor extraction, groundwater remediation, landfill gas recovery, and wastewater treatment. Vacuum pumps facilitate the removal and containment of gases, vapors, and pollutants, contributing to environmental protection and sustainable waste management.
8. Medical and Healthcare: The medical and healthcare sectors utilize vacuum pumps for various purposes. They are used in medical equipment such as vacuum-assisted wound therapy devices, vacuum-based laboratory analyzers, and vacuum suction systems in hospitals and clinics. Vacuum pumps are also used in medical research, pharmaceutical production, and medical device manufacturing.
9. Power Generation: Vacuum pumps play a role in power generation industries, including nuclear power plants and thermal power plants. They are used for steam condensation, turbine blade cooling, vacuum drying during transformer manufacturing, and vacuum systems for testing and maintenance of power plant equipment.
10. HVAC and Refrigeration: The HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) and refrigeration industries rely on vacuum pumps for system installation, maintenance, and repair. Vacuum pumps are used to evacuate air and moisture from refrigerant lines and HVAC systems, ensuring optimal system performance and efficiency.
These are just a few examples of industries that commonly rely on vacuum pump technology. The versatility and wide-ranging applications of vacuum pumps make them indispensable tools across numerous sectors, enabling precise control over vacuum conditions, efficient manufacturing processes, and scientific investigations.


editor by Dream 2024-05-08
China Standard 2be High Quality Wholesale Horizontal Impeller 5HP Mono Block Water Liquid Ring Vacuum Pump with Best Sales
Product Description
Product Description
2BE liquid ring vacuum pump is CHINAMFG liquid ring vacuum pump and is used to transport gases and vapors, predominantly for intake pressures below atmospheric pressure. Our 2BE liquid ring vacuum pump is available in 20 models, and is ATEX Certified. It offered It offered Suction capacity from 150 to 38000m³/h. It has reliable operation and economic power consumption. We also have 2BE pump with Partition wall in pump casing special for paper industry.
We offer same outline dimensions for bolt-on replacement and equivalent performances with original 2BV liquid ring vacuum pump.
|
ITEM |
UNIT |
Quantity |
|
Supply Ability |
per month |
2,000set |
2BE series water ring vacuum pumps and compressors are the products with high efficiency and economical power, which are manufactured by our company integrating with the advanced technology of the imported products from Germany. These series products adopt CHINAMFG and single action structure and have many advantages, such as, compact structure, convenient maintenance, reliable running, high efficiency and economical power. Comparing with the SK, 2SK, SZ series water ring vacuum pumps used widely in our country at present, the 2BE series products are the ideal replacements of them for high vacuum, low power, and running reliability
Product Series
Company Profile
Certifications
Packaging & Shipping
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | Online Service |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 1 Year |
| Oil or Not: | Oil |
| Structure: | Rotary Vacuum Pump |
| Exhauster Method: | Entrapment Vacuum Pump |
| Vacuum Degree: | High Vacuum |
| Samples: |
US$ 10000/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

What Is the Impact of Altitude on Vacuum Pump Performance?
The performance of vacuum pumps can be influenced by the altitude at which they are operated. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Altitude refers to the elevation or height above sea level. As the altitude increases, the atmospheric pressure decreases. This decrease in atmospheric pressure can have several effects on the performance of vacuum pumps:
1. Reduced Suction Capacity: Vacuum pumps rely on the pressure differential between the suction side and the discharge side to create a vacuum. At higher altitudes, where the atmospheric pressure is lower, the pressure differential available for the pump to work against is reduced. This can result in a decrease in the suction capacity of the vacuum pump, meaning it may not be able to achieve the same level of vacuum as it would at lower altitudes.
2. Lower Ultimate Vacuum Level: The ultimate vacuum level, which represents the lowest pressure that a vacuum pump can achieve, is also affected by altitude. As the atmospheric pressure decreases with increasing altitude, the ultimate vacuum level that can be attained by a vacuum pump is limited. The pump may struggle to reach the same level of vacuum as it would at sea level or lower altitudes.
3. Pumping Speed: Pumping speed is a measure of how quickly a vacuum pump can remove gases from a system. At higher altitudes, the reduced atmospheric pressure can lead to a decrease in pumping speed. This means that the vacuum pump may take longer to evacuate a chamber or system to the desired vacuum level.
4. Increased Power Consumption: To compensate for the decreased pressure differential and achieve the desired vacuum level, a vacuum pump operating at higher altitudes may require higher power consumption. The pump needs to work harder to overcome the lower atmospheric pressure and maintain the necessary suction capacity. This increased power consumption can impact energy efficiency and operating costs.
5. Efficiency and Performance Variations: Different types of vacuum pumps may exhibit varying degrees of sensitivity to altitude. Oil-sealed rotary vane pumps, for example, may experience more significant performance variations compared to dry pumps or other pump technologies. The design and operating principles of the vacuum pump can influence its ability to maintain performance at higher altitudes.
It’s important to note that vacuum pump manufacturers typically provide specifications and performance curves for their pumps based on standardized conditions, often at or near sea level. When operating a vacuum pump at higher altitudes, it is advisable to consult the manufacturer’s guidelines and consider any altitude-related limitations or adjustments that may be necessary.
In summary, the altitude at which a vacuum pump operates can have an impact on its performance. The reduced atmospheric pressure at higher altitudes can result in decreased suction capacity, lower ultimate vacuum levels, reduced pumping speed, and potentially increased power consumption. Understanding these effects is crucial for selecting and operating vacuum pumps effectively in different altitude environments.

How Do Vacuum Pumps Affect the Performance of Vacuum Chambers?
When it comes to the performance of vacuum chambers, vacuum pumps play a critical role. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Vacuum chambers are enclosed spaces designed to create and maintain a low-pressure environment. They are used in various industries and scientific applications, such as manufacturing, research, and material processing. Vacuum pumps are used to evacuate air and other gases from the chamber, creating a vacuum or low-pressure condition. The performance of vacuum chambers is directly influenced by the characteristics and operation of the vacuum pumps used.
Here are some key ways in which vacuum pumps affect the performance of vacuum chambers:
1. Achieving and Maintaining Vacuum Levels: The primary function of vacuum pumps is to create and maintain the desired vacuum level within the chamber. Vacuum pumps remove air and other gases, reducing the pressure inside the chamber. The efficiency and capacity of the vacuum pump determine how quickly the desired vacuum level is achieved and how well it is maintained. High-performance vacuum pumps can rapidly evacuate the chamber and maintain the desired vacuum level even when there are gas leaks or continuous gas production within the chamber.
2. Pumping Speed: The pumping speed of a vacuum pump refers to the volume of gas it can remove from the chamber per unit of time. The pumping speed affects the rate at which the chamber can be evacuated and the time required to achieve the desired vacuum level. A higher pumping speed allows for faster evacuation and shorter cycle times, improving the overall efficiency of the vacuum chamber.
3. Ultimate Vacuum Level: The ultimate vacuum level is the lowest pressure that can be achieved in the chamber. It depends on the design and performance of the vacuum pump. Higher-quality vacuum pumps can achieve lower ultimate vacuum levels, which are important for applications requiring higher levels of vacuum or for processes that are sensitive to residual gases.
4. Leak Detection and Gas Removal: Vacuum pumps can also assist in leak detection and gas removal within the chamber. By continuously evacuating the chamber, any leaks or gas ingress can be identified and addressed promptly. This ensures that the chamber maintains the desired vacuum level and minimizes the presence of contaminants or unwanted gases.
5. Contamination Control: Some vacuum pumps, such as oil-sealed pumps, use lubricating fluids that can introduce contaminants into the chamber. These contaminants may be undesirable for certain applications, such as semiconductor manufacturing or research. Therefore, the choice of vacuum pump and its potential for introducing contaminants should be considered to maintain the required cleanliness and purity of the vacuum chamber.
6. Noise and Vibrations: Vacuum pumps can generate noise and vibrations during operation, which can impact the performance and usability of the vacuum chamber. Excessive noise or vibrations can interfere with delicate experiments, affect the accuracy of measurements, or cause mechanical stress on the chamber components. Selecting vacuum pumps with low noise and vibration levels is important for maintaining optimal chamber performance.
It’s important to note that the specific requirements and performance factors of a vacuum chamber can vary depending on the application. Different types of vacuum pumps, such as rotary vane pumps, dry pumps, or turbomolecular pumps, offer varying capabilities and features that cater to specific needs. The choice of vacuum pump should consider factors such as the desired vacuum level, pumping speed, ultimate vacuum, contamination control, noise and vibration levels, and compatibility with the chamber materials and gases used.
In summary, vacuum pumps have a significant impact on the performance of vacuum chambers. They enable the creation and maintenance of the desired vacuum level, affect the pumping speed and ultimate vacuum achieved, assist in leak detection and gas removal, and influence contamination control. Careful consideration of the vacuum pump selection ensures optimal chamber performance for various applications.

What Are the Primary Applications of Vacuum Pumps?
Vacuum pumps have a wide range of applications across various industries. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Industrial Processes:
Vacuum pumps play a vital role in numerous industrial processes, including:
– Vacuum Distillation: Vacuum pumps are used in distillation processes to lower the boiling points of substances, enabling separation and purification of various chemicals and compounds.
– Vacuum Drying: Vacuum pumps aid in drying processes by creating a low-pressure environment, which accelerates moisture removal from materials without excessive heat.
– Vacuum Packaging: Vacuum pumps are used in the food industry to remove air from packaging containers, prolonging the shelf life of perishable goods by reducing oxygen exposure.
– Vacuum Filtration: Filtration processes can benefit from vacuum pumps to enhance filtration rates by applying suction, facilitating faster separation of solids and liquids.
2. Laboratory and Research:
Vacuum pumps are extensively used in laboratories and research facilities for various applications:
– Vacuum Chambers: Vacuum pumps create controlled low-pressure environments within chambers for conducting experiments, testing materials, or simulating specific conditions.
– Mass Spectrometry: Mass spectrometers often utilize vacuum pumps to create the necessary vacuum conditions for ionization and analysis of samples.
– Freeze Drying: Vacuum pumps enable freeze-drying processes, where samples are frozen and then subjected to a vacuum, allowing the frozen water to sublimate directly from solid to vapor state.
– Electron Microscopy: Vacuum pumps are essential for electron microscopy techniques, providing the necessary vacuum environment for high-resolution imaging of samples.
3. Semiconductor and Electronics Industries:
High vacuum pumps are critical in the semiconductor and electronics industries for manufacturing and testing processes:
– Semiconductor Fabrication: Vacuum pumps are used in various stages of chip manufacturing, including deposition, etching, and ion implantation processes.
– Thin Film Deposition: Vacuum pumps create the required vacuum conditions for depositing thin films of materials onto substrates, as done in the production of solar panels, optical coatings, and electronic components.
– Leak Detection: Vacuum pumps are utilized in leak testing applications to detect and locate leaks in electronic components, systems, or pipelines.
4. Medical and Healthcare:
Vacuum pumps have several applications in the medical and healthcare sectors:
– Vacuum Assisted Wound Closure: Vacuum pumps are used in negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT), where they create a controlled vacuum environment to promote wound healing and removal of excess fluids.
– Laboratory Equipment: Vacuum pumps are essential in medical and scientific equipment such as vacuum ovens, freeze dryers, and centrifugal concentrators.
– Anesthesia and Medical Suction: Vacuum pumps are utilized in anesthesia machines and medical suction devices to create suction and remove fluids or gases from the patient’s body.
5. HVAC and Refrigeration:
Vacuum pumps are employed in the HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) and refrigeration industries:
– Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Systems: Vacuum pumps are used during system installation, maintenance, and repair to evacuate moisture and air from refrigeration and air conditioning systems, ensuring efficient operation.
– Vacuum Insulation Panels: Vacuum pumps are utilized in the manufacturing of vacuum insulation panels, which offer superior insulation properties for buildings and appliances.
6. Power Generation:
Vacuum pumps play a role in power generation applications:
– Steam Condenser Systems: Vacuum pumps are used in power plants to remove non-condensable gases from steam condenser systems, improving thermal efficiency.
– Gas Capture: Vacuum pumps are utilized to capture and remove gases, such as hydrogen or helium, in nuclear power plants, research reactors, or particle accelerators.
These are just a few examples of the primary applications of vacuum pumps. The versatility and wide range of vacuum pump types make them essential in numerous industries, contributing to various manufacturing processes, research endeavors, and technological advancements.


editor by Dream 2024-05-07
China OEM GWSP300 0.55kw oil-free dry scroll vacuum pump used in labs sold to the USA,Southeast Asia and Europe with Great quality
Product Description
Product Description
GWSP Oil free Scroll Vacuum Pump
Working principle:
GWSP oil free scroll vacuum pump is constructed with pump head assembly, crank pin assembly, bracket assembly, air flush assembly,and exhaust valve assembly.Two spiral cylinders, 1 offset and orbiting against the other fixed with an offset of 180° to form several crescent-shaped pockets of different sizes. By means of an eccentric drive, the orbiting scroll is made to orbit about the fixed scroll, reducing the volume of the pockets and compressing gas from outside towards the inside thereby pumping the gas from vacuum chamber.
Basic informations:
1) Model: GWSP300 Oil free scroll vacuum pump
2) Ultimate vacuum pressure: 2.6 Pa/0.026 mbar (abs.)
3) Max suction capacity: 50Hz-4.3L/s 60Hz-5.1L/s
Safety Precautions:
The GWSP series oil free scroll vacuum pumps are suitable for clean processes only.
Do not pump toxic, explosive, flammable or corrosive substances or substances which contain chemicals, solvents or particles.GEOWELL will not perform maintenance work on pumps which have used special gases or other hazardous substances.
Be sure the inlet gas temperature must be lower than 122 °F.
Technical Specifications
| Model | GWSP40 | GWSP75 | GWSP150 | GWSP300 | GWSP600 | GWSP1000 | ||
| Pumping Speed | 50Hz | l/s | 0.5 | 1.0 | 2.0 | 4.3 | 8.7 | 16.6 |
| m3/h | 1.8 | 3.6 | 7.2 | 15.5 | 31.3 | 59.8 | ||
| cfm | 1.1 | 2.1 | 4.3 | 9.3 | 18.7 | 35.8 | ||
| 60Hz | l/s | 0.6 | 1.2 | 2.4 | 5.1 | 10.4 | 20.0 | |
| m3/h | 2.2 | 4.3 | 8.6 | 18.3 | 37.4 | 71.6 | ||
| cfm | 1.3 | 2.5 | 5.1 | 10.9 | 22.3 | 42.8 | ||
| Ultimate Pressure | Torr | ≤1.1*10-1 | ≤6.0*10-2 | ≤4.5*10-2 | ≤1.9*10-2 | ≤7.5*10-3 | ≤7.5*10-3 | |
| psi | ≤2.2*10-3 | ≤1.2*10-3 | ≤9.0*10-4 | ≤3.8*10-4 | ≤1.5*10-4 | ≤1.5*10-4 | ||
| Pa | ≤15 | ≤8 | ≤6 | ≤2.6 | ≤1 | ≤1 | ||
| mbar | ≤1.5*10-1 | ≤8.0*10-2 | ≤6.0*10-2 | ≤2.6*10-2 | ≤1.0*10-2 | ≤1.0*10-2 | ||
| Noise Level | dB(A) | ≤54 | ≤57 | ≤57 | ≤60 | ≤61 | ≤65 | |
| Leakage | mbar·l/s | 1*10-7 | ||||||
| Max. Inlet/Exhaust Pressure | MPa | 0.1 / 0.13 | ||||||
| Ambient Operation Temp. | ºF | 41~104 | ||||||
| Motor 1 phase | Power | kW | 0.25 | 0.55 | 0.55 | 0.55 | 0.75 | — |
| Voltage | V | 110~115 (60Hz),200~230 (50Hz) | — | |||||
| Speed | rpm | 1425(50Hz),1725(60Hz) | — | |||||
| Plug | North America, Europe, UK/Ireland, India | — | ||||||
| Motor 3 phase | Power | kW | — | 0.55 | 0.55 | 0.55 | 0.75 | 1.5 |
| Voltage | V | — | 200~230 or 380~415 (50Hz),200~230 or 460 (60Hz) | |||||
| Speed | rpm | — | 1425 (50Hz),1725 (60Hz) | |||||
| Inlet/Exhaust Flange | KF25/KF16 | KF40/KF16 | KF40/KF16*2 | |||||
| Dimensions | 1 phase | mm | 326*212*253 | 450*260*296 | 455*260*296 | 493*297*334 | 538*315*348 | — |
| 3 phase | mm | — | 450*260*296 | 455*260*296 | 493*297*334 | 538*315*348 | 576*450*402 | |
| Net Weight | 1 phase | kg | 15 | 21 | 22 | 29 | 36 | — |
| 3 phase | kg | — | 20 | 21 | 28 | 31 | 54 | |
| Cooling Type | Air cooled | |||||||
| Others | With air flush | |||||||
Features & Benefits
No oil clean vacuum.
No oil back-diffusion, no oil mist exhaust, provide clean vacuum environment
Wide product lineup.
Pumping speed covers 3~60 m3 /h, limited vacuum level 1~8 Pa
Suitable for all type of power supply around the world.
110/220/380/460V, 50/60Hz for choose
Low vibration, low noise.
57~65 dB(A), smooth operation
High efficiency, ease of maintenance.
No water cooled, no oil lubricated, no daily maintenance
Quality Control
CMM inspection system assures
fixed tolarance on dimension&shape
Pump Testing
Applications
Analyzing instrument and device.
Spectroscopy/scHangZhou electron microscopy.
Space environment simulation machine.
Helium Leak detector.
Mass spectrometer.
Cryopump regeneration.
Accelerators/synchrotrons.
Food and drug industry.
Freezing dryer.
Vacuum storage.
Medical equipment
Low temperature plasma sterilizer.
Vacuum storage.
Dental equipment.
Vacuum equipment.
Oil free ultrahigh vacuum unit
Oil free vacuum unit
Related Products
GWT25 Foreline Filter
Performance: Filter out the dust particles contained in the intake gas.
Application: Vacuum coating, food and drug processing, ceramic and glass manufacturing, vacuum CHINAMFG and vacuum packaging systems.
GWS16 Exhaust Silencer
Performance: Reduce exhaust noise from oil-free vacuum systems.
Application: Installation of oil free scroll vacuum pumps requires a quiet vacuum system.
GWMMK300 Major Maintenance Kit
Performance: Prolong the service life of the product.
Application: For the major maintenance of oil free scroll vacuum pump GWSP300.
GWTSK300 Tip Seal Kit
Performance: Prolong the service life of the product.
Application: For the scheduled maintenance of oil free scroll vacuum pump GWSP300.
Company Profile
GEOWELL VACUUM CO.,LTD. is a HI-TECH enterprise in China dedicating in manufacturing, research and development, marketing of oil free scroll vacuum pumps and vacuum compressors since 2002. GEOWELL has been providing users and partners with premium quality products that are efficient and dependable, GEOWELL believe the integration of high performance and high reliability product and service will bring the highest value to both our customers and ourselves.
FAQ
Q: How long can I get the feedback after we sent the inquiry?
A: We will reply you within 12 hours in working day.
Q: Are you direct manufacturer?
A: Yes, we are direct manufacturer with factory and international department; we manufacture and sell all our products by ourselves.
Q: When can you delivery the product to us?
A: Since we are a factory with large warehouse, we have abundant products in store, so we can delivery within 7 days after get your deposit.
Q: Can I add logo to the products?
A: Of course, but we usually have quantity requirement. You can contact with us for details.
Q: How to guarantee the quality and after sales service of your products?
A: We conduct strict detection during production from raw material come in to product delivering shipment. Every product must go through 4 steps inspection from casting, machining, assembling, and performance testing within our factory before shipment, also intact packaging test are insured.
Q: What is your warranty term?
A: There is a 12 months warranty for our export products from the date of shipment. If warranty has run out, our customer should pay for the replacement part.
Q: Is the sample available?
A: Yes, usually we send our samples by Fedex, DHL, TNT, UPS, EMS, SF, Depon, it will take around 3 to 4 days for our customer receive them, but customer will charge all cost related to the samples, such as sample cost and air freight. We will refund our customer the sample cost after receiving the order.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | Yes |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 1 Year |
| Oil or Not: | Oil Free |
| Structure: | Scroll Pump |
| Exhauster Method: | a Pair of Vortex Plates |
| Vacuum Degree: | Low Vacuum |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

How Are Vacuum Pumps Employed in the Production of Electronic Components?
Vacuum pumps play a crucial role in the production of electronic components. Here’s a detailed explanation:
The production of electronic components often requires controlled environments with low or no atmospheric pressure. Vacuum pumps are employed in various stages of the production process to create and maintain these vacuum conditions. Here are some key ways in which vacuum pumps are used in the production of electronic components:
1. Deposition Processes: Vacuum pumps are extensively used in deposition processes, such as physical vapor deposition (PVD) and chemical vapor deposition (CVD), which are commonly employed for thin film deposition on electronic components. These processes involve the deposition of materials onto substrates in a vacuum chamber. Vacuum pumps help create and maintain the necessary vacuum conditions required for precise and controlled deposition of the thin films.
2. Etching and Cleaning: Etching and cleaning processes are essential in the fabrication of electronic components. Vacuum pumps are used to create a vacuum environment in etching and cleaning chambers, where reactive gases or plasmas are employed to remove unwanted materials or residues from the surfaces of the components. The vacuum pumps help evacuate the chamber and ensure the efficient removal of byproducts and waste gases.
3. Drying and Bake-out: Vacuum pumps are utilized in the drying and bake-out processes of electronic components. After wet processes, such as cleaning or wet etching, components need to be dried thoroughly. Vacuum pumps help create a vacuum environment that facilitates the removal of moisture or solvents from the components, ensuring their dryness before subsequent processing steps. Additionally, vacuum bake-out is employed to remove moisture or other contaminants trapped within the components’ materials or structures, enhancing their reliability and performance.
4. Encapsulation and Packaging: Vacuum pumps are involved in the encapsulation and packaging stages of electronic component production. These processes often require the use of vacuum-sealed packaging to protect the components from environmental factors such as moisture, dust, or oxidation. Vacuum pumps assist in evacuating the packaging materials, creating a vacuum-sealed environment that helps maintain the integrity and longevity of the electronic components.
5. Testing and Quality Control: Vacuum pumps are utilized in testing and quality control processes for electronic components. Some types of testing, such as hermeticity testing, require the creation of a vacuum environment for evaluating the sealing integrity of electronic packages. Vacuum pumps help evacuate the testing chambers, ensuring accurate and reliable test results.
6. Soldering and Brazing: Vacuum pumps play a role in soldering and brazing processes for joining electronic components and assemblies. Vacuum soldering is a technique used to achieve high-quality solder joints by removing air and reducing the risk of voids, flux residuals, or oxidation. Vacuum pumps assist in evacuating the soldering chambers, creating the required vacuum conditions for precise and reliable soldering or brazing.
7. Surface Treatment: Vacuum pumps are employed in surface treatment processes for electronic components. These processes include plasma cleaning, surface activation, or surface modification techniques. Vacuum pumps help create the necessary vacuum environment where plasma or reactive gases are used to treat the component surfaces, improving adhesion, promoting bonding, or altering surface properties.
It’s important to note that different types of vacuum pumps may be used in electronic component production, depending on the specific process requirements. Commonly used vacuum pump technologies include rotary vane pumps, turbo pumps, cryogenic pumps, and dry pumps.
In summary, vacuum pumps are essential in the production of electronic components, facilitating deposition processes, etching and cleaning operations, drying and bake-out stages, encapsulation and packaging, testing and quality control, soldering and brazing, as well as surface treatment. They enable the creation and maintenance of controlled vacuum environments, ensuring precise and reliable manufacturing processes for electronic components.

Can Vacuum Pumps Be Used in the Production of Solar Panels?
Yes, vacuum pumps are extensively used in the production of solar panels. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Solar panels, also known as photovoltaic (PV) panels, are devices that convert sunlight into electricity. The manufacturing process of solar panels involves several critical steps, many of which require the use of vacuum pumps. Vacuum technology plays a crucial role in ensuring the efficiency, reliability, and quality of solar panel production. Here are some key areas where vacuum pumps are utilized:
1. Silicon Ingot Production: The first step in solar panel manufacturing is the production of silicon ingots. These ingots are cylindrical blocks of pure crystalline silicon that serve as the raw material for solar cells. Vacuum pumps are used in the Czochralski process, which involves melting polycrystalline silicon in a quartz crucible and then slowly pulling a single crystal ingot from the molten silicon. Vacuum pumps create a controlled environment by removing impurities and preventing contamination during the crystal growth process.
2. Wafering: After the silicon ingots are produced, they undergo wafering, where the ingots are sliced into thin wafers. Vacuum pumps are used in wire saws to create a low-pressure environment that helps to cool and lubricate the cutting wire. The vacuum also assists in removing the silicon debris generated during the slicing process, ensuring clean and precise cuts.
3. Solar Cell Production: Vacuum pumps play a significant role in various stages of solar cell production. Solar cells are the individual units within a solar panel that convert sunlight into electricity. Vacuum pumps are used in the following processes:
– Diffusion: In the diffusion process, dopants such as phosphorus or boron are introduced into the silicon wafer to create the desired electrical properties. Vacuum pumps are utilized in the diffusion furnace to create a controlled atmosphere for the diffusion process and remove any impurities or gases that may affect the quality of the solar cell.
– Deposition: Thin films of materials such as anti-reflective coatings, passivation layers, and electrode materials are deposited onto the silicon wafer. Vacuum pumps are used in various deposition techniques like physical vapor deposition (PVD) or chemical vapor deposition (CVD) to create the necessary vacuum conditions for precise and uniform film deposition.
– Etching: Etching processes are employed to create the desired surface textures on the solar cell, which enhance light trapping and improve efficiency. Vacuum pumps are used in plasma etching or wet etching techniques to remove unwanted material or create specific surface structures on the solar cell.
4. Encapsulation: After the solar cells are produced, they are encapsulated to protect them from environmental factors such as moisture and mechanical stress. Vacuum pumps are used in the encapsulation process to create a vacuum environment, ensuring the removal of air and moisture from the encapsulation materials. This helps to achieve proper bonding and prevents the formation of bubbles or voids, which could degrade the performance and longevity of the solar panel.
5. Testing and Quality Control: Vacuum pumps are also utilized in testing and quality control processes during solar panel production. For example, vacuum systems can be used for leak testing to ensure the integrity of the encapsulation and to detect any potential defects or leaks in the panel assembly. Vacuum-based measurement techniques may also be employed for assessing the electrical characteristics and efficiency of the solar cells or panels.
In summary, vacuum pumps are integral to the production of solar panels. They are used in various stages of the manufacturing process, including silicon ingot production, wafering, solar cell production (diffusion, deposition, and etching), encapsulation, and testing. Vacuum technology enables precise control, contamination prevention, and efficient processing, contributing to the production of high-quality and reliable solar panels.
Are There Different Types of Vacuum Pumps Available?
Yes, there are various types of vacuum pumps available, each designed to suit specific applications and operating principles. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Vacuum pumps are classified based on their operating principles, mechanisms, and the type of vacuum they can generate. Some common types of vacuum pumps include:
1. Rotary Vane Vacuum Pumps:
– Description: Rotary vane pumps are positive displacement pumps that use rotating vanes to create a vacuum. The vanes slide in and out of slots in the pump rotor, trapping and compressing gas to create suction and generate a vacuum.
– Applications: Rotary vane vacuum pumps are widely used in applications requiring moderate vacuum levels, such as laboratory vacuum systems, packaging, refrigeration, and air conditioning.
2. Diaphragm Vacuum Pumps:
– Description: Diaphragm pumps use a flexible diaphragm that moves up and down to create a vacuum. The diaphragm separates the vacuum chamber from the driving mechanism, preventing contamination and oil-free operation.
– Applications: Diaphragm vacuum pumps are commonly used in laboratories, medical equipment, analysis instruments, and applications where oil-free or chemical-resistant vacuum is required.
3. Scroll Vacuum Pumps:
– Description: Scroll pumps have two spiral-shaped scrolls—one fixed and one orbiting—which create a series of moving crescent-shaped gas pockets. As the scrolls move, gas is continuously trapped and compressed, resulting in a vacuum.
– Applications: Scroll vacuum pumps are suitable for applications requiring a clean and dry vacuum, such as analytical instruments, vacuum drying, and vacuum coating.
4. Piston Vacuum Pumps:
– Description: Piston pumps use reciprocating pistons to create a vacuum by compressing gas and then releasing it through valves. They can achieve high vacuum levels but may require lubrication.
– Applications: Piston vacuum pumps are used in applications requiring high vacuum levels, such as vacuum furnaces, freeze drying, and semiconductor manufacturing.
5. Turbo Molecular Vacuum Pumps:
– Description: Turbo pumps use high-speed rotating blades or impellers to create a molecular flow, continuously pumping gas molecules out of the system. They typically require a backing pump to operate.
– Applications: Turbo molecular pumps are used in high vacuum applications, such as semiconductor fabrication, research laboratories, and mass spectrometry.
6. Diffusion Vacuum Pumps:
– Description: Diffusion pumps rely on the diffusion of gas molecules and their subsequent removal by a high-speed jet of vapor. They operate at high vacuum levels and require a backing pump.
– Applications: Diffusion pumps are commonly used in applications requiring high vacuum levels, such as vacuum metallurgy, space simulation chambers, and particle accelerators.
7. Cryogenic Vacuum Pumps:
– Description: Cryogenic pumps use extremely low temperatures to condense and capture gas molecules, creating a vacuum. They rely on cryogenic fluids, such as liquid nitrogen or helium, for operation.
– Applications: Cryogenic vacuum pumps are used in ultra-high vacuum applications, such as particle physics research, material science, and fusion reactors.
These are just a few examples of the different types of vacuum pumps available. Each type has its advantages, limitations, and suitability for specific applications. The choice of vacuum pump depends on factors like required vacuum level, gas compatibility, reliability, cost, and the specific needs of the application.


editor by Dream 2024-05-06
China Good quality Value Vacuum Pump in Stainless Steel 304-316-2205 Material vacuum pump ac system
Product Description
COMPANY SHOW:
20 Years
ZiBo ZhuoXin Pump Industry co,.Ltd is located in a century industrial city known as the Pump Capital of China—HangZhou city, ZheJiang Province. Has over 20 years’ experience of manufacturing vacuum pumps and 10+ years’ experience of exporting.
Various products
We can suppply all type of vacuum pumps and spare parts in China, 2BV/2BEA/2BEC/SK/2SK/JZJ2B/ etc, and other industrial machine;
24 Hours
Please do not hestiate to contact us if have any urgent matters,each of your inquiries will be taken into account and get our response within 24 hours.
Product Main feature:
2BVC series water ring vacuum pumps and compressor is mainly used for sucking gases and water vapor .The ultimate suction pressure can reach 33mbar (abs) (i.e. 97 degree). When the liquid ring vacuum pumps work under the condition near the limited vacuum for a long time, it is necessary to connect with the cavitation resistant pipe in order to get rid of the screaming and protect the pump.
We are offering 2bvc series liquid ring vacuum pumps.
MAIN APPLICATION AREAS:
- Vacuum filtering – Chemical filtering factories, chemical processing factories, iron ore factory, mining, phosphorite, paper making, poultry processing, coal-selecting factories.
- Vacuum distillation – milk factory, foodstuff processing, chemical industry, the paper plasma factory.
- Vacuum disinfection – hospital, infirmary, the laboratory.
- Molding – Plastic, the polyethylene, rubber, tire manufacture etc.
- Rebirth the compressed air – the paper plasma, iron and steel, automobile, glasses, chemical industry.
| Product model | Maximum air volume | Limit Vacuum Degree mbar(MPa) |
Motor power kW |
Explosion-proof grade of motor | Motor Protection Level | Pump speed r.p.m |
Working fluid flow rate L/min |
noise dB(A) |
Weight kg |
|
| m3/min | m3/h | |||||||||
| 2BVC2 060 | 0.45 | 27 | 33mbar (-0.098MPa) |
0.81 | No explosion proof | IP54 | 2840 | 2 | 62 | 31 |
| 2BVC2 061 | 0.87 | 52 | 1.45 | 2840 | 2 | 65 | 35 | |||
| 2BVC2 070 | 1.33 | 80 | 2.35 | 2860 | 2.5 | 66 | 56 | |||
| 2BVC2 071 | 1.83 | 110 | 3.85 | 2880 | 4.2 | 72 | 65 | |||
| 2BVC2 060-Ex | 0.45 | 27 | 1.1 | – | IP55 | 2840 | 2 | 62 | 39 | |
| 2BVC2 061-Ex | 0.86 | 52 | 1.5 | 2840 | 2 | 65 | 45 | |||
| 2BVC2 070-Ex | 1.33 | 80 | 3 | 2860 | 2.5 | 66 | 66 | |||
| 2BVC2 071-Ex | 1.83 | 110 | 4 | 2880 | 4.2 | 72 | 77 | |||
| 2BVC5 110 | 2.75 | 165 | 4 | No explosion proof | IP54 | 1440 | 6.7 | 63 | 103 | |
| 2BVC5 111 | 3.83 | 230 | 5.5 | 1440 | 8.3 | 68 | 117 | |||
| 2BVC5 121 | 4.67 | 280 | 7.5 | 1440 | 10 | 69 | 149 | |||
| 2BVC5 131 | 6.67 | 400 | 11 | 1460 | 15 | 73 | 205 | |||
| 2BVC5 161 | 8.33 | 500 | 15 | 970 | 20 | 74 | 331 | |||
| 2BVC6 110-EX | 2.75 | 165 | 4 | dIIBT4 | IP55 | 1440 | 6.7 | 63 | 153 | |
| 2BVC6 111-EX | 3.83 | 230 | 5.5 | 1440 | 8.3 | 68 | 208 | |||
| 2BVC6 121-EX | 4.66 | 280 | 7.5 | 1440 | 10 | 69 | 240 | |||
| 2BVC6 131-EX | 6.66 | 400 | 11 | 1460 | 15 | 73 | 320 | |||
| 2BVC6 161-EX | 8.33 | 500 | 15 | 970 | 20 | 74 | 446 | |||
2bv series of vacuum pumps adopt the advance international technology with the close-coupled design. With the advantages of high reliable performance, easy maintenance, lower noise, high efficiency and energy saving, this series of pumps are widely applied in fields of chemical industry, papermaking, and metallurgy industry and so on.
Due to its competitive price and higher performance, our pump is best choice for CZPT and some italy pump replacement.
FAQ
Q: What’s your MOQ?
A: One set;
Q: What are the causes of no flow or insufficient flow of centrifugal pump?
A: There is air in the suction pipe or pump, which needs to be discharged. Air leakage is found in the suction pipeline, and the leakage is repaired. If the valve of suction line or discharge line is closed, relevant valve shall be opened. If the suction height is too high, recalculate the installation height. The suction line is too small or blocked.
Q: How to resist cavitation in centrifugal pump?
A: Improve the structure design from the suction to the impeller of the centrifugal pump;Adopt double stage suction impeller and use anti-cavitation material;
Q:What is the function of rubber ball in water ring vacuum pump?
A: Rubber ball in water ring vacuum pump, the correct name is called rubber ball valve. Its role is to eliminate the pump equipment in the operation process of the phenomenon of over compression or insufficient compression.
Q:How long is warranty?
A:One year formain construction warranty.
Q:How can I pay for my items? What is the payment you can provide
A:Usually by T/T, 30%-50% deposit payment once PI/Contract confirmed, then the remaining balance will be paid after inspection and before shipment via T/T or L/C;
Welcome client from home and abroad to contact us for future cooperation.
Detail size drawing and install drawing please contact our sales in charge to get;
Key:nash/simense/refurish/vacuum pumps/HangZhou CZPT pump/ /* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | 1 Year |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 1 Year |
| Oil or Not: | Oil Free |
| Structure: | Reciprocating Vacuum Pump |
| Exhauster Method: | Positive Displacement Pump |
| Vacuum Degree: | High Vacuum |
| Samples: |
US$ 0/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|

What Are Vacuum Pumps?
Vacuum pumps use air flow as the source of energy. The system is ideal for dewatering wet media, creating filter cakes, and pneumatically moving materials through a pipe. A vacuum pump works through air flow that is moved by differential pressure. The pump’s air flow develops a vacuum in a chamber that is called the vacuum box. As the air flow collects gas at a faster rate than atmospheric pressure, it is considered the “heart” of a vacuum system.
Principles of operation
Vacuum pumps work by reducing the volume of air that moves through them. Depending on the design, there are several different types of vacuum pumps. All of these types operate under the same principles, but have their own special features. Here are some of their most important characteristics. In addition to their capacity, the main differences between these pumps are their manufacturing tolerances, materials of construction, and level of tolerance for chemicals, oil vapor, and vibration.
Vacuum pumps create a partial or low-pressure vacuum by forcing gas molecules from their high-pressure states to their low-pressure states. However, these pumps can only achieve a partial vacuum, and other methods are necessary to reach a higher level of vacuum. As with all pumps, there are several ways to increase the level of a vacuum.
First, consider the type of vacuum you want. This is the most important factor when choosing a vacuum pump. If you need a high level of vacuum, you’ll need a high-quality vacuum pump. High-quality vacuum pumps have a high pressure limit, while ultrahigh-quality pumps are capable of achieving a very low vacuum. As the pressure decreases, the amount of molecules per cubic centimeter decreases and the quality of the vacuum increases.
Positive displacement pumps are best suited for low and medium-pressure systems. But they can’t reach high vacuum, which is why most high-pressure systems use two pumps in tandem. In this case, the positive displacement pump would stall and the other one would be used instead. Similarly, entrapment pumps have higher-pressure limits, so they must be refreshed frequently or exhaust frequently when there is too much gas to capture.
Another important aspect of vacuum pump operation is its speed. The speed of pumping is proportional to the differential pressure across the system. Therefore, the faster the pumping speed, the lower the draining time.
Design
A vacuum pump is a mechanical device used to generate a vacuum. It can create a low or high vacuum. These pumps are used in the process of oil regeneration and re-refining. The design of a vacuum pump must be compatible with the vacuum. The pump’s mass and speed should be matched.
The design of a vacuum pump is important for many reasons. It should be easy to use and maintain. Vacuum pumps need to be protected from external contamination. For this reason, the oil must be kept clean at all times. Contamination may damage the oil, resulting in pump failure. The pump’s design should include features that will prevent this from happening.
The main objective of a vacuum pump is to remove air and other gases from a chamber. As the pressure of the chamber drops, the amount of molecules that can be removed becomes more difficult. Because of this, industrial and research vacuum systems typically require pumps to operate over a large pressure range. The range is generally between one and 10-6 Torr. A standard vacuum system uses multiple pumps, each covering a portion of the pressure range. These pumps can also be operated in a series to achieve optimal performance.
The design of a vacuum pump can vary depending on the application and the pressure requirement. It should be sized appropriately to ensure that it works properly. There are several different types of pumps, so selecting the right pump is essential to maximizing its efficiency. For example, a slow running vee belt drive rotary vane vacuum pump will have a lower running temperature than a fast-running direct-drive pump.
Performance
The performance of a vacuum pump is an important indicator of its overall condition. It helps determine whether the system is performing optimally and how high the ultimate vacuum level can be achieved. A performance log should be maintained to document variations in pump operating hours and voltage as well as the temperature of the pump’s cooling water and oil. The log should also record any problems with the pump.
There are several ways to increase the performance of a vacuum pump. For example, one way is to decrease the temperature of the working fluid. If the temperature of the fluid is too high, it will lead to a low vacuum. A high temperature will make the vacuum degree of the pump even lower, so heat transfer is an important part of the process.
Nozzles are another major component that impacts the performance of a vacuum pump. Damage or clogging can result in a compromised pumping capacity. These problems can occur due to a number of causes, including excessive noise, leakage, and misassembled parts. Nozzles can also become clogged due to rusting, corrosion, or excess water.
Performance of vacuum pump technology is vital for many industries. It is an integral part of many central production processes. However, it comes with certain expenses, including machines, installations, energy, and maintenance. This makes it essential to understand what to look for when purchasing a vacuum pump. It is important to understand the factors that can influence these factors, as they affect the efficiency of a vacuum pump.
Another important factor in determining the performance of a vacuum pump is throughput. Throughput is a measurement of how many molecules can be pumped per unit of time at a constant temperature. Moreover, throughput can also be used to evaluate volume leak rates and pressure at the vacuum side. In this way, the efficiency of a vacuum pump can be judged by the speed and throughput of its leaks.
Atmospheric pressure
Vacuum pumps work by sucking liquids or air into a container. The amount of vacuum a pump can create is measured in pressure units called atms (atmospheric pressure). The pressure of a vacuum pump is equal to the difference between atmospheric pressure and the pressure in the system.
The amount of force produced by air molecules on each other is proportional to the number of impacts. Therefore, the greater the impact, the higher the pressure. In addition, all molecules have the same amount of energy at any temperature. This holds true for both pure and mixture gases. However, lighter molecules will move faster than heavier ones. Nevertheless, the transfer of energy is the same for both.
The difference between atmospheric and gauge pressure is not always straightforward. Some applications use one term to describe the other. While the two concepts are closely related, there are key differences. In most cases, atmospheric pressure is a higher number than gauge pressure. As a result, it can be confusing when choosing a vacuum pump.
One method is to use a U-tube manometer, a compact device that measures the difference between atmospheric pressure and vacuum. This device is commonly used for monitoring vacuum systems. It can measure both negative and positive pressure. In addition, it uses an electronic version of a gauge.
The atmospheric pressure affects the performance of a vacuum pump. When working with porous materials, the pump must overcome leakage. As a result, it must be equipped with enough capacity to compensate for variations in the porosity of the work piece. This is why it is critical to buy a vacuum pump that has a large enough capacity to handle the variation.
Typical application
Vacuum pumps are used in a variety of applications. They generate low and high pressures and are used to evaporate water or gases from various materials. They are also used in petroleum regeneration and re-refining processes. Typical applications of vacuum pumps include: a.
b. Rotary vane pumps are used in a variety of vacuum applications. They are suitable for industrial applications, freeze drying and cabinet making. They use oil as a sealant and coolant, allowing them to perform well in a variety of applications. This makes them ideal for use in a variety of industries.
The pumping rate of the vacuum pump is important. This refers to the volume pumped from a given point at a given rate. The higher the speed, the faster the pump will expel the air. Depending on the gas composition, this number will vary. When choosing a vacuum pump, gas composition and process requirements should be considered.
Vacuum pumps are used in a variety of industries from laboratories to medical facilities. In medical applications, they are used in radiation therapy and radiopharmaceuticals. They are also used in mass spectrometers, which are instruments used to analyze solid, liquid, or surface materials. Vacuum pumps are also used in decorative vacuum coatings and Formula 1 engine components. A trash compactor is another example of using a vacuum pump.
Vacuum pumps are used in a variety of applications including water purification and aeration. Vacuum pumps are also used in portable dental equipment and compressors in the dental industry. Vacuum pumps are also used in molds for dental implants. Other common applications for vacuum pumps include soil aeration and air sampling.


editor by Dream 2024-05-06
China OEM CZPT Chinese Factory High Quality 2.5HP Gasoline Water Pump vacuum pump diy
Product Description
Product Description
| Inlet and outlet inside DI. (mm) | 25.4 |
| Pump lift | 30m |
| Suction height | 8m |
| Max. Capacity | 8m3/h |
| Corresponding rationbed speed | 7000rmp |
| Fuel tank capacity | 0.5L |
| Start model | Hand operated |
| Engine type | Air-cooled, 4-stroke, single cylinder gasoline |
| Engine model | 139F |
| Net weight | 8.5kg |
| Size of product | 42*27.5*37.5CM |
ZHangZhoug CZPT Power Machinery Co., Ltd. is a well-known supplier of customized outboard motors. The company is located in Xihu (West Lake) Dis. District, HangZhou City, ZHangZhoug Province–Xihu (West Lake) Dis.hai, a rising commercial city along the coast. Our factory specializes in the production of outboard motors, garden machinery, agricultural machinery, and plastic products. It is a private enterprise integrating technology, industry and trade. With the concept of “capital as the link, high technology as the guide, people-oriented, market as the carrier”, our company continues to develop and grow, and strives to be the best. In order to establish a corporate culture based on “performance-oriented, learning-oriented organization” and centering on the corporate vision of “creating a world garden and creating a world brand”, we adhere to “excellent quality, reliable reputation, and famous brand” and actively pursue sustainable development. In the new century, CZPT people will continue to strive for self-improvement, build CZPT brand with high quality and high standards, and participate in international competition. All staff of CZPT warmly welcome your visit, call or inquiry. Let us join hands to create a better future.
FAQ
Q1:Do you provide OEM service? Can we put our own logo on the machine?
A1:Yes, we offer OEM service. We can customized the logo, carton design, user manual, etc for you if you order a large quantity.
Q2: Are you a factory or trading company?
A2: We are a factory, which has been specializing in the production of outboard motors and garden machinery for almost 20 years.
Q3: Can I get a sample to test the quality?
A3: Yes, you can request for a sample, but we will charge the sample fee. When you place official bulk order, we can refund the fee to you.
Q4: What’s the lead time?
A4: For the products in stock, we can send out the goods within 72 hours, and the goods out of stock will usually be completed within 15-30 days after receiving your advance payment. If you need a large quantity, you need to negotiate with our sales.
Q5: What is your terms of delivery?
A5: FOB, CFR, CIF, DDU.
Q6: Do you test all your goods before delivery?
A6: Yes, we have 100% test before delivery.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Material: | Alu. |
|---|---|
| Structure: | Piston Pump |
| Assembly: | Liquid Pumps |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|
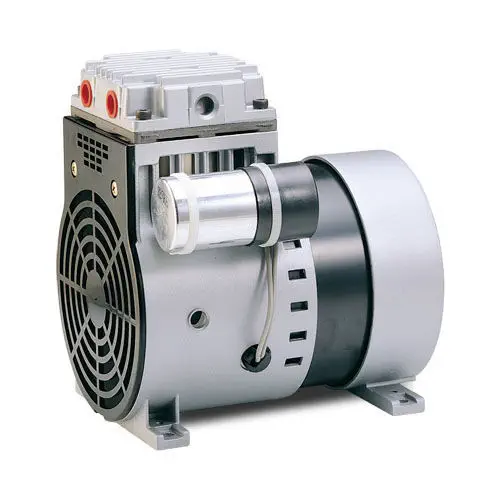

What Are the Typical Applications of Piston Vacuum Pumps?
Piston vacuum pumps find applications in various industries and processes. Here’s a detailed explanation of the typical applications of piston vacuum pumps:
1. Laboratories and Research Facilities:
– Piston vacuum pumps are commonly used in laboratories and research facilities for a wide range of applications.
– They are utilized in vacuum ovens, freeze dryers, vacuum filtration systems, and other equipment requiring controlled evacuation.
2. Pharmaceuticals and Biotechnology:
– In the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries, piston vacuum pumps are employed for processes such as solvent evaporation, distillation, and filtration.
– They are used in drug manufacturing, vaccine production, and research involving biochemistry and molecular biology.
3. Food Processing and Packaging:
– Piston vacuum pumps play a vital role in the food processing and packaging industry.
– They are used in vacuum packaging machines to remove air from packaging containers, extending the shelf life of food products.
4. HVAC and Refrigeration Systems:
– Piston vacuum pumps are utilized in HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems and refrigeration systems.
– They help evacuate air and moisture from the systems to achieve the desired pressure and prevent contamination.
5. Manufacturing and Industrial Processes:
– Piston vacuum pumps are employed in various manufacturing and industrial processes.
– They are used for degassing, vacuum impregnation, vacuum drying, and other applications that require controlled evacuation.
6. Automotive Industry:
– In the automotive industry, piston vacuum pumps are often used in brake booster systems.
– They create a vacuum to assist in brake actuation, providing the necessary power for braking.
7. Electronics and Semiconductor Manufacturing:
– Piston vacuum pumps are utilized in electronics and semiconductor manufacturing processes.
– They help create a controlled environment with low-pressure conditions during the production of microchips, integrated circuits, and other electronic components.
8. Environmental Monitoring and Analysis:
– Piston vacuum pumps are utilized in environmental monitoring and analysis equipment.
– They are used in air sampling devices, gas analyzers, and other instruments that require precise vacuum control.
9. Scientific Research and Vacuum Systems:
– Piston vacuum pumps are employed in various scientific research applications.
– They are used in vacuum systems for particle accelerators, electron microscopes, mass spectrometers, surface analysis instruments, and other scientific equipment.
In summary, piston vacuum pumps have diverse applications in laboratories, pharmaceuticals, food processing, HVAC systems, manufacturing processes, automotive industry, electronics, environmental monitoring, scientific research, and more. Their ability to provide controlled evacuation and achieve moderate vacuum levels makes them suitable for a wide range of industries and processes.
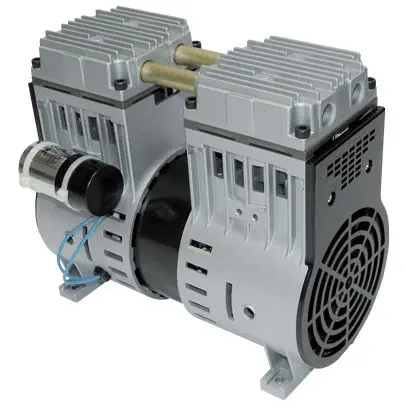

Are There Noise Considerations When Using Piston Vacuum Pumps?
Yes, there are noise considerations to take into account when using piston vacuum pumps. Here’s a detailed explanation:
– Piston vacuum pumps can generate noise during their operation, which is important to consider, especially in environments where noise levels need to be minimized.
– The noise produced by piston vacuum pumps is primarily caused by mechanical vibrations and the movement of internal components.
– The noise level can vary depending on factors such as the design and construction of the pump, the speed of operation, and the load conditions.
– Excessive noise from piston vacuum pumps can have several implications:
– Occupational Health and Safety: High noise levels can pose a risk to the health and safety of operators and personnel working in the vicinity of the pump. Prolonged exposure to loud noise can lead to hearing damage and other related health issues.
– Environmental Impact: In certain settings, such as residential areas or noise-sensitive locations, excessive noise from piston vacuum pumps may result in noise pollution and non-compliance with local noise regulations.
– Equipment Interference: Noise generated by the pump can interfere with the operation of nearby sensitive equipment, such as electronic devices or precision instruments, potentially affecting their performance.
– To mitigate the noise produced by piston vacuum pumps, several measures can be taken:
– Enclosures and Sound Insulation: Installing acoustic enclosures or sound-insulating materials around the pump can help contain and reduce the noise. These enclosures are designed to absorb or block the sound waves generated by the pump.
– Vibration Isolation: Using vibration isolation mounts or pads can help minimize the transmission of vibrations from the pump to surrounding structures, reducing the noise level.
– Maintenance and Lubrication: Regular maintenance, including lubrication of moving parts, can help reduce friction and mechanical noise generated by the pump.
– Operating Conditions: Adjusting the operating conditions of the pump, such as speed and load, within the manufacturer’s specified limits can help optimize performance and minimize noise generation.
– Location and Placement: Proper positioning and placement of the pump, considering factors such as distance from occupied areas or sensitive equipment, can help minimize the impact of noise.
– It is important to consult the manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations regarding noise levels and any specific measures to mitigate noise for a particular piston vacuum pump model.
– Compliance with local regulations and standards regarding noise emissions should also be considered and adhered to.
In summary, noise considerations are important when using piston vacuum pumps to ensure the health and safety of personnel, minimize environmental impact, and prevent interference with other equipment. Measures such as enclosures, vibration isolation, maintenance, and proper operating conditions can help mitigate the noise generated by these pumps.

What Are the Differences Between Single-Stage and Two-Stage Piston Vacuum Pumps?
Single-stage and two-stage piston vacuum pumps are two common types of pumps used for creating a vacuum. Here’s a detailed explanation of their differences:
1. Number of Stages:
– The primary difference between single-stage and two-stage piston vacuum pumps lies in the number of stages or steps involved in the compression process.
– A single-stage pump has a single piston that compresses the gas in one stroke.
– In contrast, a two-stage pump consists of two pistons arranged in series, allowing the gas to be compressed in two stages.
2. Compression Ratio:
– Single-Stage: In a single-stage piston vacuum pump, the compression ratio is limited to the single stroke of the piston. This means that the pump can achieve a compression ratio of approximately 10:1.
– Two-Stage: In a two-stage piston vacuum pump, the compression ratio is significantly higher. The first stage compresses the gas, and then it passes through an intermediate chamber before entering the second stage for further compression. This allows for a higher compression ratio, typically around 100:1.
3. Vacuum Level:
– Single-Stage: Single-stage piston vacuum pumps are generally suitable for applications that require moderate vacuum levels.
– They can achieve vacuum levels up to approximately 10-3 Torr (millitorr) or in the low micron range (10-6 Torr).
– Two-Stage: Two-stage piston vacuum pumps are capable of reaching deeper vacuum levels compared to single-stage pumps.
– They can achieve vacuum levels in the high vacuum range, typically down to 10-6 Torr or even lower, making them suitable for applications that require a more extensive vacuum.
4. Pumping Speed:
– Single-Stage: Single-stage pumps generally have a higher pumping speed or evacuation rate compared to two-stage pumps.
– This means that single-stage pumps can evacuate a larger volume of gas per unit of time, making them suitable for applications that require faster evacuation.
– Two-Stage: Two-stage pumps have a lower pumping speed compared to single-stage pumps.
– While they may have a slower evacuation rate, they compensate for it by achieving deeper vacuum levels.
5. Applications:
– Single-Stage: Single-stage piston vacuum pumps are commonly used in applications that require moderate vacuum levels and higher pumping speeds.
– They are suitable for laboratory use, vacuum packaging, HVAC systems, and various industrial processes.
– Two-Stage: Two-stage piston vacuum pumps are well-suited for applications that require deeper vacuum levels.
– They are commonly used in scientific research, semiconductor manufacturing, analytical instruments, and other processes that demand high vacuum conditions.
6. Size and Complexity:
– Single-Stage: Single-stage pumps are generally more compact and simpler in design compared to two-stage pumps.
– They have fewer components, making them easier to install, operate, and maintain.
– Two-Stage: Two-stage pumps are relatively larger and more complex in design due to the additional components required for the two-stage compression process.
– They may require more maintenance and expertise for operation and servicing.
In summary, the main differences between single-stage and two-stage piston vacuum pumps lie in the number of stages, compression ratio, achievable vacuum levels, pumping speed, applications, and size/complexity. Selecting the appropriate pump depends on the desired vacuum level, pumping speed requirements, and specific application needs.


editor by Dream 2024-05-06
China high quality Cryogenic Vacuum Submersible Liquid LNG Air Pump vacuum pump distributors
Product Description
Cryogenic Vacuum Submersible Liquid LNG Air Pump
Liquids pumped:
LN2,LAr,LNG
Technical Parameters
1. flow rate: 2-20 m3/h
2. Lift: 30-300M
Application
LNG gas filling stations,LNG gas receiving station
Cylinder filling, Tank filling
Cryogenic liquid transfer
Zero leakage case
Optional configuration
Vacuum adiabatic set
Frequency converter
Features
1.The pump and motor submerged totally in the liquid to reduce the liquid lost from the heat and make the quick start possible.
2.Vaccum adiabatic set prevent the liquid from the heat outside to make the pump work well
3.Special design with no seal set and submerged reduce the chance of maintain
4.The vertical type makes the motor a better performance and long lifetime.
5.Motor with frequency converter expand the working range.
Instruction
The adjustable frequency speed motor expanded the work range, so the cryogenic submerged pump is widely used by gas filling stations and LNG terminals, for cylinder filling and LNG delivery. The applicable gases are LNG, liquid nitrogen and liquid argon.
WHAT WE CAN SUPPLY?
We specialize in producing air separation plants, CO2 recovery plants, cryogenic liquid storage tanks, ISO tanks, semi-trailer tankers, vaporizers, gas filling stations, cylinders and dewars, dry ice machines, compressors and cryogenic pumps etc.
Our Company
HangZhou CZPT General Equipment Co.,Ltd. is a wholly owned subsidiary of ZheJiang Air Separation Plant Group Company-the second largest gas equipment producer in China.
In the gas equipment field, we are proficient in both design and manufacture, enjoying a good reputation worldwide. By our consistent efforts, we turned the invisible air into visible brilliance. With 40 years of experience, we can provide customers with a complete range of products and the most professional services.
Taking advantage of the group company structure, we have an in-depth and comprehensive understanding of market. Customers can get all they need at one-stop purchase.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Oil or Not: | Oil Free |
|---|---|
| Structure: | Piston Pump |
| Exhauster Method: | Centrifugal Pump |
| Usage: | Pump |
| Flow: | 500-1500L/H |
| Medium: | LNG |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

How Does a Piston Vacuum Pump Work?
A piston vacuum pump, also known as a reciprocating vacuum pump, operates using a piston mechanism to create a vacuum. Here’s a detailed explanation of its working principle:
1. Piston and Cylinder Assembly:
– A piston vacuum pump consists of a piston and cylinder assembly.
– The piston is a movable component that fits inside the cylinder and creates a seal between the piston and cylinder walls.
2. Intake and Exhaust Valves:
– The cylinder has two valves: an intake valve and an exhaust valve.
– The intake valve allows gas or air to enter the cylinder during the suction stroke, while the exhaust valve allows the expelled gas to exit during the compression stroke.
3. Suction Stroke:
– During the suction stroke, the piston moves downward, creating a vacuum within the cylinder.
– As the piston moves down, the intake valve opens, allowing gas or air from the system being evacuated to enter the cylinder.
– The volume within the cylinder increases, causing a decrease in pressure and the creation of a partial vacuum.
4. Compression Stroke:
– After the suction stroke, the piston moves upward during the compression stroke.
– As the piston moves up, the intake valve closes, preventing backflow of gas into the evacuated system.
– Simultaneously, the exhaust valve opens, allowing the gas trapped in the cylinder to be expelled.
– The upward movement of the piston reduces the volume within the cylinder, compressing the gas and increasing its pressure.
5. Expulsion of Gas:
– Once the compression stroke is complete, the gas is expelled through the exhaust valve.
– The exhaust valve then closes, ready for the next suction stroke.
– This process of alternating suction and compression strokes continues, gradually reducing the pressure within the evacuated system.
6. Lubrication:
– Piston vacuum pumps require lubrication for smooth operation and to maintain the airtight seal between the piston and cylinder walls.
– Lubricating oil is often introduced into the cylinder to provide lubrication and help maintain the seal.
– The oil also helps to cool the pump by dissipating heat generated during operation.
7. Applications:
– Piston vacuum pumps are commonly used in applications where high vacuum levels and low flow rates are required.
– They are suitable for processes such as laboratory work, vacuum drying, vacuum filtration, and other applications that require moderate vacuum levels.
In summary, a piston vacuum pump operates by creating a vacuum through the reciprocating motion of a piston within a cylinder. The suction stroke creates a vacuum by lowering the pressure within the cylinder, while the compression stroke expels the gas and increases its pressure. This cyclic process continues, gradually reducing the pressure within the system being evacuated. Piston vacuum pumps are commonly used in various applications that require moderate vacuum levels and low flow rates.
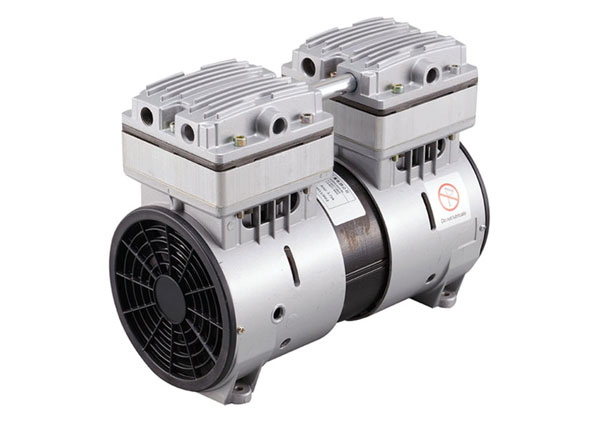

What Are the Safety Precautions for Operating Piston Vacuum Pumps?
Operating piston vacuum pumps requires adherence to safety precautions to ensure the well-being of personnel and the proper functioning of the equipment. Here’s a detailed explanation of the safety precautions for operating piston vacuum pumps:
– Familiarize Yourself with the User Manual: Before operating a piston vacuum pump, thoroughly read and understand the user manual provided by the manufacturer. The manual contains important safety guidelines specific to the pump model.
– Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment, such as safety goggles, gloves, and hearing protection, when operating the pump. This helps protect against potential hazards, including chemical exposure, flying debris, and noise.
– Ventilation: Ensure that the area where the pump is operated has adequate ventilation. Proper ventilation helps prevent the accumulation of fumes, vapors, or hazardous gases that may be generated during the pumping process.
– Electrical Safety: Follow electrical safety precautions, including proper grounding and connection of the pump to a suitable power source. Inspect power cords and plugs for any damage before use, and avoid using the pump in wet or damp environments.
– Pressure and Vacuum Limits: Operate the pump within its specified pressure and vacuum limits. Exceeding these limits can lead to equipment failure, compromising safety and performance.
– Overpressure Protection: Ensure the pump has appropriate overpressure protection mechanisms, such as relief valves or pressure sensors, to prevent excessive pressure buildup. Regularly inspect and maintain these safety devices to ensure their proper functioning.
– Cooling and Temperature: Pay attention to the cooling requirements of the pump. Adequate cooling is necessary to prevent overheating and potential damage to the pump. Avoid blocking or obstructing cooling vents or fins. Monitor the pump’s temperature during operation and follow any temperature-related guidelines provided by the manufacturer.
– Maintenance and Inspection: Regularly inspect and maintain the pump according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. This includes cleaning, lubricating, and replacing parts as necessary. Perform maintenance tasks only when the pump is turned off and disconnected from the power source.
– Emergency Stop: Familiarize yourself with the location and operation of the emergency stop button or switch on the pump. In case of any emergency or abnormal situation, immediately activate the emergency stop to shut down the pump safely.
– Training and Competence: Ensure that operators are adequately trained and competent to operate the piston vacuum pump. Proper training helps minimize the risks associated with incorrect operation or handling of the equipment.
– Hazardous Materials: If the pump is used with hazardous materials, follow appropriate safety protocols for handling, containment, and disposal. Be aware of the potential risks associated with the materials being pumped and take necessary precautions to mitigate those risks.
– Warning Signs and Labels: Pay attention to warning signs, labels, and markings on the pump, including safety instructions, hazard warnings, and operating instructions. Follow these instructions carefully to ensure safe operation.
– Emergency Procedures: Establish and communicate clear emergency procedures in case of accidents, spills, or other hazardous situations. Ensure that operators are aware of these procedures and know how to respond appropriately.
– Regular Risk Assessment: Conduct regular risk assessments of the pump operation to identify potential hazards and implement appropriate safety measures. Periodically review and update safety protocols based on the results of these assessments.
– Emergency Response Resources: Keep appropriate emergency response resources readily available, such as fire extinguishers, spill kits, and emergency eyewash stations, in case of accidents or spills.
In summary, operating piston vacuum pumps safely requires following several key safety precautions, including familiarizing yourself with the user manual, using appropriate personal protective equipment, ensuring proper ventilation, adhering to electrical safety guidelines, operating within pressure and vacuum limits, maintaining cooling requirements, performing regular maintenance and inspections, being aware of emergency stop procedures, providing adequate training and competence, handling hazardous materials safely, paying attention to warning signs and labels, establishing emergency procedures, conducting risk assessments, and keeping emergency response resources available.

What Are the Differences Between Single-Stage and Two-Stage Piston Vacuum Pumps?
Single-stage and two-stage piston vacuum pumps are two common types of pumps used for creating a vacuum. Here’s a detailed explanation of their differences:
1. Number of Stages:
– The primary difference between single-stage and two-stage piston vacuum pumps lies in the number of stages or steps involved in the compression process.
– A single-stage pump has a single piston that compresses the gas in one stroke.
– In contrast, a two-stage pump consists of two pistons arranged in series, allowing the gas to be compressed in two stages.
2. Compression Ratio:
– Single-Stage: In a single-stage piston vacuum pump, the compression ratio is limited to the single stroke of the piston. This means that the pump can achieve a compression ratio of approximately 10:1.
– Two-Stage: In a two-stage piston vacuum pump, the compression ratio is significantly higher. The first stage compresses the gas, and then it passes through an intermediate chamber before entering the second stage for further compression. This allows for a higher compression ratio, typically around 100:1.
3. Vacuum Level:
– Single-Stage: Single-stage piston vacuum pumps are generally suitable for applications that require moderate vacuum levels.
– They can achieve vacuum levels up to approximately 10-3 Torr (millitorr) or in the low micron range (10-6 Torr).
– Two-Stage: Two-stage piston vacuum pumps are capable of reaching deeper vacuum levels compared to single-stage pumps.
– They can achieve vacuum levels in the high vacuum range, typically down to 10-6 Torr or even lower, making them suitable for applications that require a more extensive vacuum.
4. Pumping Speed:
– Single-Stage: Single-stage pumps generally have a higher pumping speed or evacuation rate compared to two-stage pumps.
– This means that single-stage pumps can evacuate a larger volume of gas per unit of time, making them suitable for applications that require faster evacuation.
– Two-Stage: Two-stage pumps have a lower pumping speed compared to single-stage pumps.
– While they may have a slower evacuation rate, they compensate for it by achieving deeper vacuum levels.
5. Applications:
– Single-Stage: Single-stage piston vacuum pumps are commonly used in applications that require moderate vacuum levels and higher pumping speeds.
– They are suitable for laboratory use, vacuum packaging, HVAC systems, and various industrial processes.
– Two-Stage: Two-stage piston vacuum pumps are well-suited for applications that require deeper vacuum levels.
– They are commonly used in scientific research, semiconductor manufacturing, analytical instruments, and other processes that demand high vacuum conditions.
6. Size and Complexity:
– Single-Stage: Single-stage pumps are generally more compact and simpler in design compared to two-stage pumps.
– They have fewer components, making them easier to install, operate, and maintain.
– Two-Stage: Two-stage pumps are relatively larger and more complex in design due to the additional components required for the two-stage compression process.
– They may require more maintenance and expertise for operation and servicing.
In summary, the main differences between single-stage and two-stage piston vacuum pumps lie in the number of stages, compression ratio, achievable vacuum levels, pumping speed, applications, and size/complexity. Selecting the appropriate pump depends on the desired vacuum level, pumping speed requirements, and specific application needs.


editor by Dream 2024-05-03